Home Heating Solutions
Sustainable Home Heating: An Array of Heat Pump Options

Are you tired of expensive and environmentally damaging traditional heating options? Look no further! We provide a revolutionary solution to revolutionize the way you heat your home.
In this article, we will explore the array of heat pump options available for sustainable home heating. From air source heat pumps to ground source heat pumps and ductless mini-split heat pumps, we’ll cover all the innovative technologies that can help you achieve efficient and eco-friendly home heating.
Get ready to embrace the future of heating!
Key Takeaways
- Geothermal heat pumps utilize the earth’s constant temperature for efficient heating and tap into geothermal energy for reliable and environmentally friendly heating.
- Hybrid heat pumps combine traditional heating methods with modern heat pump technology, allowing for greater flexibility and efficiency in switching between different energy sources based on weather conditions.
- Air source heat pumps offer high energy efficiency, versatility in heating and cooling functions, easy installation, and lower initial investment compared to ground source heat pumps.
- Ground source heat pumps offer significant reduction in energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions, although they require a costly installation, they are a worthwhile investment for sustainable heating.
Types of Heat Pumps for Sustainable Home Heating
We’ll now explore the various types of heat pumps available for sustainable home heating.

When it comes to sustainable heating solutions, geothermal heat pumps and hybrid heat pumps are at the forefront of innovation. Geothermal heat pumps utilize the earth’s constant temperature to efficiently heat your home. By tapping into the earth’s natural heat, these pumps provide reliable and environmentally friendly heating.
On the other hand, hybrid heat pumps combine the best of both worlds by integrating traditional heating methods with modern heat pump technology. This allows for greater flexibility and efficiency, as the heat pump can switch between different energy sources depending on the weather conditions.
When choosing a heat pump for your home, factors such as energy efficiency, cost, and climate should be considered. By carefully evaluating these factors, you can ensure that you select the most suitable heat pump for your sustainable home heating needs.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Heat Pump for Your Home
When choosing a heat pump for our homes, there are two important factors we should consider: cost and efficiency, as well as size and capacity. Cost and efficiency play a crucial role in determining the long-term savings and environmental impact of our heating system.

Size and capacity, on the other hand, are essential to ensure that the heat pump can effectively meet our heating needs without being oversized or undersized.
Cost and Efficiency
One important factor to consider when choosing a heat pump for our home is the cost and efficiency of the system. The cost effectiveness of a heat pump refers to its ability to provide heating and cooling at a reasonable price. Heat pumps are known for their energy efficiency, as they can extract heat from the air, ground, or water sources and transfer it indoors. This reduces the reliance on fossil fuels and minimizes the environmental impact of our home heating system.
When considering the cost and efficiency of a heat pump, there are several key factors to keep in mind:
- Energy efficiency rating: Look for heat pumps with high SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) and HSPF (Heating Seasonal Performance Factor) ratings.
- Operating costs: Consider the long-term savings on energy bills that come with a highly efficient heat pump.
- Installation and maintenance costs: Evaluate the upfront costs of purchasing and installing a heat pump, as well as the ongoing maintenance expenses.
- Rebates and incentives: Check if there are any government or utility rebates or incentives available to offset the cost of purchasing a heat pump.
- Environmental impact: Assess the carbon footprint and environmental impact of different heat pump models.
Considering these factors will help us make an informed decision about the cost effectiveness and environmental impact of our home heating system.

Now let’s move on to the next crucial factor: size and capacity.
Size and Capacity
The size and capacity of a heat pump are important factors to consider when choosing the right one for our home. Heating capacity refers to the amount of heat a pump can produce, while sizing options determine the appropriate size of the heat pump for our specific needs. It is crucial to select a heat pump with the correct heating capacity to ensure optimal comfort and energy efficiency.
To help you make an informed decision, we have provided a table below showcasing various sizing options for heat pumps:
| Sizing Option | Suitable for |
|---|---|
| Small | Apartments or small homes |
| Medium | Average-sized homes |
| Large | Large homes or commercial buildings |
| Extra Large | Multi-level or spacious homes |
Pros and Cons of Air Source Heat Pumps for Home Heating
We have evaluated the pros and cons of air source heat pumps for home heating. Here are the key points to consider:

-
Energy Efficiency: Air source heat pumps are highly efficient, converting energy from the air into heat, which reduces energy consumption and lowers utility bills.
-
Versatility: These heat pumps can both heat and cool your home, providing year-round comfort.
-
Easy Installation: Air source heat pumps are relatively easy to install and require less space compared to ground source heat pumps.
-
Cost-effective: The initial investment for an air source heat pump is lower than that of a ground source heat pump, making it a more affordable option.

-
Environmental Impact: Air source heat pumps produce fewer greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional heating systems, contributing to a greener and more sustainable future.
Now that we’ve explored the benefits and drawbacks of air source heat pumps, let’s move on to exploring ground source heat pumps for efficient home heating.
Exploring Ground Source Heat Pumps for Efficient Home Heating
Let’s delve into the benefits and considerations of ground source heat pumps for efficient home heating.
Ground source heat pumps, also known as geothermal heat pumps, utilize the constant temperature of the earth to provide heating and cooling for residential buildings. The main advantage of these systems is their ability to tap into geothermal energy, which is a renewable and sustainable source of heat. By harnessing the earth’s natural heat, ground source heat pumps can significantly reduce energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional heating methods.

The installation process for ground source heat pumps involves burying a series of underground pipes, known as a ground loop, in the ground near the home. These pipes are filled with a heat transfer fluid that absorbs the heat from the ground and carries it into the heat pump system. The heat pump then uses this heat to warm the air or water that’s circulated throughout the home.
While the installation process can be more complex and costly compared to other heating systems, the long-term energy savings and environmental benefits make it a worthwhile investment for those seeking sustainable home heating solutions.
How Ductless Mini-Split Heat Pumps Can Revolutionize Home Heating
One option we should consider for revolutionizing home heating is by utilizing ductless mini-split heat pumps. These innovative devices offer several advantages that can greatly improve energy efficiency and reduce the environmental impact of heating systems.
Here are five reasons why ductless mini-split heat pumps are a game-changer:

-
Energy savings: Ductless mini-split heat pumps are highly efficient, allowing homeowners to save on their energy bills while keeping their homes warm.
-
Zoned heating: These systems allow for independent temperature control in different areas of the house, ensuring personalized comfort and further energy savings.
-
Easy installation: Unlike traditional heating systems, ductless mini-split heat pumps don’t require extensive ductwork, making installation quick and hassle-free.
-
Improved indoor air quality: With no ducts to collect dust and allergens, these heat pumps provide cleaner and healthier air for you and your family.

-
Eco-friendly: By using electricity as their power source, ductless mini-split heat pumps produce fewer greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuel-based heating systems.
With their energy savings and positive environmental impact, ductless mini-split heat pumps are a smart choice for sustainable home heating.
Now, let’s explore other innovative heat pump technologies for even more efficient and eco-friendly heating solutions.
Innovative Heat Pump Technologies for Sustainable Home Heating
Two innovative heat pump technologies offer sustainable home heating solutions: ground source heat pumps and air source heat pumps.

Ground source heat pumps, also known as geothermal heat pumps, utilize the constant temperature of the earth to provide heating for homes. These pumps extract heat from the ground through a loop system and transfer it to the home through a heat exchanger. This technology is highly efficient and can significantly reduce energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions.
On the other hand, air source heat pumps extract heat from the outside air and transfer it into the home. These pumps are versatile and can be easily installed in both new and existing homes.
Additionally, hybrid heat pumps combine the benefits of both ground source and air source heat pumps to maximize efficiency and performance.
These innovative heat pump technologies provide sustainable and cost-effective heating solutions for homes, making them an excellent choice for those seeking innovative and environmentally-friendly options.

Frequently Asked Questions
Are Heat Pumps Cost-Effective Compared to Traditional Heating Systems?
Heat pumps are cost-effective compared to traditional heating systems. Their high efficiency reduces energy consumption, resulting in lower utility bills. Additionally, heat pumps have a lower environmental impact, making them a sustainable choice for home heating.
How Long Does It Take for a Heat Pump to Heat up a Home?
It takes a heat pump varying amounts of time to heat up a home depending on its efficiency and factors like insulation and weather conditions. The efficiency of a heat pump is crucial in ensuring quick and effective heating.
Can Heat Pumps Be Used for Cooling During the Summer Months?
Yes, heat pumps can be used for cooling during the summer months. They provide efficient cooling by transferring heat from indoors to outdoors. This is one of the advantages of heat pumps in summer.
Are There Any Government Incentives or Rebates Available for Installing a Heat Pump?
Yes, there are government incentives and rebates available for heat pump installation. These incentives and rebates aim to encourage the adoption of sustainable home heating solutions and make them more accessible to homeowners.

What Maintenance Is Required for Heat Pumps and How Often Should It Be Done?
Maintaining heat pumps is crucial for optimal efficiency. Regular maintenance, such as cleaning filters and checking refrigerant levels, should be done yearly. Trust us, a well-maintained heat pump will keep your home cozy without breaking the bank.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the wide range of heat pump options available for sustainable home heating offers an array of choices for homeowners. By carefully considering factors such as efficiency and cost, individuals can choose the heat pump that best suits their needs.
Whether it’s the convenience of an air source heat pump, the efficiency of a ground source heat pump, or the versatility of a ductless mini-split heat pump, these innovative technologies are revolutionizing home heating.
Embrace the future of sustainable heating and make a positive impact on the environment.

Home Heating Solutions
A Step-by-Step Guide to Calculating Your Heat Pump Energy Savings
Prepare to uncover how much you could save with a heat pump, but first, let’s dive into the essential calculations and factors to consider.

To calculate your heat pump energy savings, start by checking the annual energy usage of your current heating system. Then, look at your heat pump's efficiency rating. You can compare them to see potential savings. Consider factors like your home size, insulation quality, and local climate, as they heavily influence energy demands. Typically, you might save around $370 a year, but some see savings up to $1,000. Take note of installation costs and federal tax credits, too. Understanding these factors prepares you for big savings, and there's plenty more to explore as you enhance your efficiency.
Key Takeaways
- Determine your current heating system's annual energy use to establish a baseline for comparison with a heat pump's efficiency.
- Calculate the heat pump's estimated annual energy consumption based on its efficiency rating, considering your home's size and local climate.
- Assess potential energy savings by comparing your current system's costs with the heat pump's projected energy expenses over a year.
- Factor in installation costs, including potential federal tax credits, to evaluate the overall financial impact and payback period.
- Review your home's weatherization quality and make necessary improvements to maximize the heat pump's efficiency and energy savings.
Understanding Heat Pump Energy Use
Understanding how heat pumps use energy is vital for maximizing their efficiency and savings. When you consider heat pump installation, it's important to know that these systems typically consume between 400 kWh to 22,500 kWh annually. The average heat pump uses around 5,475 kWh, comparable to powering nine full-size refrigerators!
This energy use can vary greatly based on your home size, climate, and insulation quality. Regular maintenance and correct installation are key factors that contribute to optimizing energy consumption, as the impact of maintenance can dramatically enhance the overall efficiency of your heat pump.
One of the standout features of heat pumps is their impressive energy efficiency. Operating at approximately 250% efficiency (sCOP 2.5), they produce more heat energy than the electrical energy they consume. This means for every unit of electricity, you can expect more than double in heating output.
To maximize your bill savings, you can achieve accurate energy use estimates through load calculations or by adjusting your historical energy bills based on efficiency ratings.
As you embrace home electrification, understanding these factors helps optimize your heating system's performance, leading to lower energy costs and greater comfort in your home.
Factors Influencing Energy Savings

Several key factors influence the energy savings you can achieve with a heat pump. Understanding these elements can help you maximize your investment and enjoy greater comfort in your home. Additionally, the choice of building materials and the overall design of your living space can also impact efficiency, particularly in tiny house construction.
- Local Climate: Colder winters and humid summers can lead to increased energy demand. This means your heat pump has to work harder, affecting overall efficiency.
- Home Size and Layout: Larger or poorly designed homes typically require more energy for heating and cooling. If your space isn't optimized, you might see less savings.
- Weatherization Quality: Proper insulation and air sealing are essential. Well-insulated homes can dramatically lower heating and cooling needs, guaranteeing your heat pump works efficiently.
When you install a heat pump, consider its efficiency ratings, like sCOP and SEER. High-efficiency models can offer up to 50% savings compared to traditional systems.
Plus, the condition of your existing HVAC system and ductwork greatly influences energy savings, so make sure everything is in good shape. By focusing on these factors, you can enhance your home's energy efficiency and enjoy significant savings on your energy bills.
Estimating Costs and Savings

Estimating the costs and savings associated with a heat pump installation can seem intimidating, but breaking it down makes it manageable.
Start by comparing the annual energy use of your current heating system to that of the heat pump. Adjust for the heat pump's efficiency rating (sCOP) to determine your potential energy savings, which can be significant, especially when you consider the benefits of converting retirement accounts for long-term financial planning. Homeowners typically save around $370 annually, with some seeing up to $1,000 in reductions when moving from inefficient systems.
Next, consider the installation costs for heat pumps, which generally range from $3,500 to $8,000. Don't forget that federal tax credits can offset up to 30% of these expenses, enhancing your overall savings.
To calculate projected energy bill savings, multiply your expected annual kWh savings by your local electricity rate.
Keep in mind that the payback period for a heat pump installation is usually around 15 years, depending on your initial installation costs and the energy savings you realize each year.
Comparing Efficiency Ratings
When evaluating heat pump installations, comparing efficiency ratings is key to maximizing your energy savings. Understanding both the Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) and the Heating Season Performance Factor (HSPF) will help you choose the best system for your home.
By taking into account various factors such as assessing risks and rewards associated with different models, you can make a more informed decision.
- Potential energy savings of up to 50% with high-efficiency models.
- Cost savings from lower energy bills each month.
- Enhanced comfort in your home year-round.
SEER measures cooling efficiency, with ratings typically ranging from 14 to 20, while HSPF indicates how efficiently a heat pump heats your space. The higher the ratings, the lower your energy consumption will be, especially when compared to traditional electric resistance systems that only operate at 100% efficiency.
Look for ENERGY STAR certified heat pumps, which meet stringent efficiency criteria from the EPA, ensuring you get superior performance.
High-efficiency models can achieve efficiencies of up to 300% under ideal conditions, making them a smart choice for energy savings.
Long-Term Financial Benefits

Investing in a heat pump can yield notable long-term financial benefits for homeowners. By upgrading to a heat pump, you could save an average of $370 on your annual energy bill, with some homeowners benefiting from savings as high as $1,000 when moving away from inefficient systems.
Credit cards play an essential role in personal finance management, allowing homeowners to finance such upgrades while managing their budgets effectively. While the installation cost of heat pumps averages around $16,000, the considerable energy savings can lead to a payback period of approximately 15 years.
Heat pumps are designed to reduce energy bills by 30-50%, providing you with significant financial savings compared to traditional heating and cooling systems. Additionally, you can enhance your savings by taking advantage of federal tax credits, which can cover up to 30% of your heat pump purchase and installation costs. This can greatly lower your upfront expenses.
Frequently Asked Questions
How to Calculate Heat Pump Energy Consumption?
To calculate your heat pump's energy consumption, find its wattage, multiply by operating hours, and convert to kilowatt-hours. Adjust for local climate and efficiency ratings to get a more accurate annual estimate.
Is It Cheaper to Leave the Heat Pump on All Day?
Keeping your heat pump on all day could save you 30% to 50% in energy costs compared to traditional heating. It's often cheaper to maintain a steady temperature rather than frequently adjusting your thermostat.
What Is the Most Economical Way to Run a Heat Pump?
To run your heat pump economically, keep a consistent temperature, use the appropriate mode for the season, maintain it regularly, consider solar power, and explore local rebates to maximize savings on your energy bills.
Is It Better to Keep a Heat Pump at a Constant Temperature?
Yes, keeping your heat pump at a constant temperature is better. It runs more efficiently this way, avoiding energy spikes. Frequent adjustments can lead to higher bills and discomfort, so set it and leave it.
Conclusion
By understanding your heat pump's energy use and the factors that influence savings, you can make informed decisions that feel like finding hidden treasure in your energy bills. Estimating costs and comparing efficiency ratings helps you see the long-term financial benefits clearly. With the right approach, you'll not only save money but also contribute to a greener planet. So, take the plunge and start calculating your heat pump energy savings today!
Home Heating Solutions
Climate Control Revolution: Why Heat Pumps Are the Future
Climate control is evolving, and heat pumps are at the forefront; discover how they could transform your energy usage and sustainability efforts.

Heat pumps are revolutionizing climate control by providing efficient heating and cooling while cutting your energy costs. They can operate three times more efficiently than traditional systems, helping reduce your greenhouse gas emissions. With advances in technology, they work effectively in colder climates, making them a smart choice for any homeowner. Plus, federal tax credits can offset installation costs considerably, making heat pumps more accessible than ever. As you explore this topic further, you'll uncover how these innovations can align with sustainability goals and potentially reshape your energy future.
Key Takeaways
- Heat pumps provide year-round heating and cooling, operating at three times the efficiency of traditional systems, promoting energy savings and sustainability.
- The Federal Inflation Reduction Act offers up to 30% tax credits for heat pump installations, making them more affordable for homeowners.
- Technological advancements have improved heat pump performance in colder climates, making them viable for a wider range of environments.
- Switching to heat pumps can save households significantly on energy bills, especially for those currently using electric resistance heating.
- Broad adoption of heat pumps aligns with climate goals, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and supporting the transition to renewable energy sources.
Understanding Heat Pumps
Heat pumps are an innovative solution for climate control, acting as both heating and cooling systems. They efficiently transfer heat from outside to inside during winter and reverse the process in summer. This versatility makes heat pumps a valuable climate control system for any home.
Unlike traditional heating solutions, heat pumps operate at up to three times the energy efficiency of natural gas or oil heating, leading to significant cost savings on energy bills.
In 2022, heat pump sales in the US surpassed gas furnace sales, showcasing a growing trend towards more sustainable heating options. Thanks to advancements in technology, heat pumps can now function effectively in various climates, even in colder temperatures, which broadens their applicability.
Moreover, the financial incentives provided by the federal Inflation Reduction Act, offering up to 30% tax credits for installation costs, make heat pumps even more appealing for homeowners.
Benefits of Heat Pumps

With the growing popularity of heat pumps, it's important to understand the many benefits they offer.
These energy-efficient appliances are three times more efficient than traditional natural gas or oil heating systems, considerably cutting down your energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions.
Additionally, advancements in innovations in heat pump technology have led to improved performance and reduced energy consumption.
One of the most appealing aspects of heat pumps is their versatility; they provide both heating and cooling, ensuring year-round comfort by efficiently transferring heat from outside to inside in winter and reversing the process in summer.
Economic Considerations

Switching to heat pumps involves traversing a complex landscape of economic considerations. While these systems promise energy efficiency and savings over time, the upfront costs can be overwhelming.
To mitigate the risks associated with high initial expenses, it's essential to research credible installation companies and understand available incentives for reducing costs, such as the tax credits for heat pumps. You need to evaluate the initial investment against long-term benefits.
Here are four key economic factors to evaluate:
- Upfront Costs: Installation of heat pumps may require a significant initial outlay, which can be a barrier for many households.
- Savings: Households currently using electric resistance heating can save up to $3,000 annually by making the switch, thanks to lower operating costs.
- Incentives: The Inflation Reduction Act provides a 30% tax credit for installation costs, potentially covering up to $8,000 for low-income families, making heat pumps more accessible.
- Economic Challenges: Rising electricity prices, which have doubled in Massachusetts in the past decade, create hurdles for heat pump adoption despite available subsidies.
Ultimately, understanding these economic factors will help you navigate the decision to embrace heat pumps as a solution to combat climate change while also being mindful of your budget.
Adoption Challenges

The journey toward widespread heat pump adoption faces several hurdles that can deter many homeowners. Rising electricity prices, which have doubled in Massachusetts over the past decade, create significant adoption challenges, especially for those relying on natural gas heating.
While switching to heat pumps can improve energy efficiency, the average annual bill increase of $400 to $500 limits the economic incentives for many families. Additionally, understanding the importance of balanced nutrition as an essential aspect of wellness can help households make informed decisions about their energy use, potentially leading to more sustainable practices.
In multi-family settings, such as apartments, your options for heat pump installation may be restricted. This can complicate shifts, requiring landlord cooperation and financing solutions to make it feasible. Without these elements, the potential benefits of heat pumps remain out of reach for many.
To encourage broader adoption, we need significant policy changes, including reductions in electricity prices and supportive measures from policymakers, utilities, and regulators. These changes are critical to help you and your neighbors take advantage of heat pumps and meet state energy goals.
Despite the existing challenges, innovative solutions like window heat pumps are emerging to offer alternatives for those living in less accessible environments. The path forward demands collective effort to overcome these obstacles.
Policy and Incentives

Addressing the challenges of heat pump adoption requires a robust framework of policies and incentives. With rising electricity prices, especially in states like Massachusetts, it's essential to create supportive measures that encourage homeowners to make the switch.
Additionally, the stability offered by investments like a Gold IRA can provide homeowners with the financial security needed to invest in energy-efficient upgrades, such as heat pumps, as a means of long-term savings and wealth preservation potential for long-term growth through gold appreciation.
Here are some key policies and incentives to reflect upon:
- Tax Credits: The Federal Inflation Reduction Act provides a 30% tax credit for heat pump installations, making it easier for many to afford this upgrade.
- Rebates: States offer various rebates to offset the initial costs, directly addressing financial barriers and promoting wider adoption.
- Targeted Assistance: Low-income households can receive up to 100% coverage for installation costs, greatly reducing economic strain.
- Collaborative Reforms: Policymakers, utilities, and regulators must work together to create a cohesive strategy that aligns with climate targets and facilitates the shift from fossil fuels.
Future Outlook

As you look ahead, technological advancements in heat pumps will likely make them even more efficient, especially in colder climates.
The integration of renewable energy sources, such as geothermal energy generation, can further enhance the overall effectiveness of heat pumps.
With strong policy support, like tax incentives and ambitious installation targets, the adoption of these systems is set to rise.
You're part of a growing movement that values sustainability and long-term savings, making heat pumps a smart choice for the future.
Technological Advancements Ahead
Innovation in heat pump technology is poised to revolutionize how we approach heating and cooling in our homes. With ongoing advancements, newer heat pumps are becoming more efficient, ensuring they perform well even in extreme cold climates.
The introduction of the Energy Star cold-climate rating encourages manufacturers to create models that excel in colder regions, making heat pumps a more appealing option for a broader audience. Additionally, as pet ownership increases, homeowners are seeking solutions that consider the well-being of their furry friends, leading to a demand for cat behavior and emotional attachment in home design.
Here are some exciting developments to look forward to:
- Multifunction Heat Pumps: These models will provide both space heating and hot water, streamlining energy consumption.
- Efficiency Upgrades: Enhanced designs will allow heat pumps to extract heat from the environment more effectively, even in low temperatures.
- Environmentally Safe Refrigerants: Ongoing research aims to minimize the environmental impact of heat pumps while maintaining their performance.
- Smart Home Integration: Innovations in smart home technology will enable you to optimize your heating and cooling schedules, leading to greater energy savings.
As these technological advancements unfold, you can expect your heating and cooling systems to become more efficient, sustainable, and user-friendly than ever before.
Policy Support Necessities
To guarantee a successful change to heat pumps, substantial policy support is imperative. As states like Massachusetts aim for over 500,000 installations by 2030, it's critical to address rising electricity costs that have doubled over the past decade. Collaborative efforts among policymakers, utilities, and regulators will help meet broader energy change goals while managing these costs.
Additionally, understanding the financial implications of adopting new technologies, such as credit card insights, can further inform consumer decisions about energy-efficient investments.
Financial incentives, such as rebates from the Federal Inflation Reduction Act, play an essential role in easing the economic burden of switching to heat pumps. For natural gas users, average annual bill increases can reach $400 to $500, making these incentives even more necessary.
Supporting low-income families through accessible financing options for heat pump installations could save them up to $3,000 annually, greatly reducing their energy expenses.
Comprehensive policy frameworks that prioritize renewable energy sources and promote energy efficiency are important for achieving climate goals. By focusing on these areas, you'll not only facilitate the widespread adoption of heat pumps but also create a more sustainable and affordable energy future for everyone.
It's time to guarantee that policy support aligns with the urgent need for a climate-friendly transformation.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why Are Heat Pumps the Future?
Heat pumps are the future because they're more efficient, cutting energy costs and emissions. You'll benefit from lower utility bills and government incentives, making them an attractive choice for sustainable home heating solutions in any climate.
Why Are HVAC Companies Pushing Heat Pumps?
Like a refreshing change, HVAC companies push heat pumps because they efficiently heat and cool homes, reduce costs, and align with growing demands for energy efficiency and sustainability, making them a smart choice for you.
What Is the Downside to a Heat Pump?
When considering a heat pump, you might face higher installation costs, potential inefficiency in extreme cold, increased annual bills, more maintenance requirements, and rising electricity prices, all of which can complicate your decision.
Are Heat Pumps More Efficient Now Than 20 Years Ago?
Yes, heat pumps are definitely more efficient now than 20 years ago. With advancements in technology, modern models offer considerably better performance, saving you more money on energy bills while providing reliable heating and cooling.
Conclusion
In the grand scheme of things, heat pumps are shaping up to be a game changer for climate control. They offer an efficient, eco-friendly way to heat and cool your home while saving you money in the long run. Sure, there are challenges to overcome, but with the right policies and incentives in place, the future looks bright. Embracing this technology now means you're not just keeping your home comfortable; you're also helping to protect the planet.
Home Heating Solutions
Heat Pump Efficiency in Green Buildings: A Comparative Study
Heat pump efficiency plays a crucial role in green buildings; discover how ASHPs and GSHPs compare and what it means for sustainable energy solutions.

When evaluating heat pump efficiency in green buildings, you'll notice a significant difference between air-source heat pumps (ASHPs) and ground-source heat pumps (GSHPs). ASHPs work best in moderate climates, often struggling in colder areas with a COP around 2.357. In contrast, GSHPs maintain a COP of about 2.44 even in chilly environments. They not only provide better energy efficiency, saving operational costs by up to 40%, but also contribute to reduced CO2 emissions. Understanding these differences can enhance your decision-making for energy-efficient solutions. There's much more to explore on this topic, so keep going to uncover additional insights.
Key Takeaways
- Heat pumps, especially GSHPs, can significantly reduce home energy use by 31% to 47%, enhancing green building efficiency.
- Ground Source Heat Pumps (GSHPs) achieve higher COP values than Air Source Heat Pumps (ASHPs), particularly in colder climates, improving overall performance.
- Regular maintenance and optimized design of heat pump systems are crucial for maximizing energy efficiency in green buildings.
- Financial incentives, such as those from the Inflation Reduction Act, facilitate the adoption of efficient heat pump systems in green construction.
- Implementing heat pumps contributes to substantial reductions in greenhouse gas emissions, aligning with sustainability goals in green building initiatives.
Overview of Heat Pump Efficiency
When it comes to energy efficiency, heat pumps stand out as a smart choice for heating and cooling in green buildings.
These systems, whether air-source heat pumps (ASHP) or ground-source heat pumps (GSHP), greatly enhance energy savings. In fact, heat pumps can achieve a coefficient of performance (COP) ranging from 1.8 to 5.0 for heating and from 4.7 to 5.7 for cooling, illustrating their ability to transfer thermal energy effectively.
Regular maintenance is vital to guarantee peak performance and efficiency over time, as common causes of heat pump failures can lead to reduced efficiency.
In colder climates, GSHPs often outperform ASHPs, boasting COP values up to 2.44, which is essential for maximizing efficiency.
The exergy efficiency of ASHPs is about 40.7% in extreme cold, while GSHPs can hit 43.2%, indicating their superior performance under challenging conditions.
Types of Heat Pump Systems
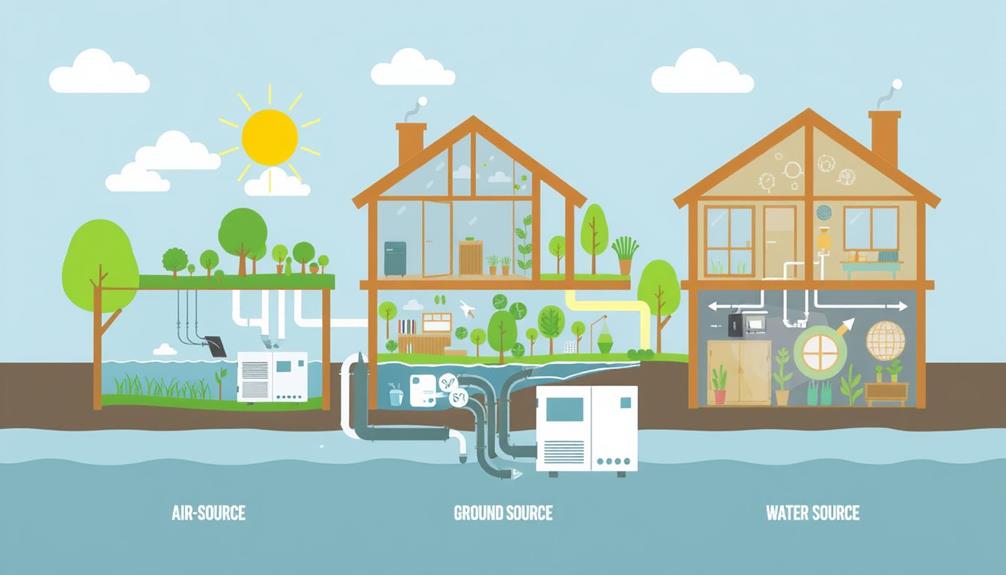
Heat pump systems come in two primary types: air-source heat pumps (ASHP) and ground-source heat pumps (GSHP). ASHPs transfer heat between indoor and outdoor air, making them particularly effective in moderate climates. They achieve a coefficient of performance (COP) ranging from 1.8 to 5.0 in heating mode, providing a reliable heating system.
In regions where renewable energy sources like geothermal energy generation can be harnessed, the performance of heat pumps can be further enhanced. On the other hand, GSHPs utilize stable underground temperatures for heat transfer, demonstrating superior heating efficiency. In colder regions, GSHPs can outperform ASHPs by up to 70%, making them an excellent choice for maximizing thermal comfort.
Both types of heat pumps offer significant energy efficiency and operational cost savings compared to traditional HVAC systems. GSHPs can deliver cost savings of up to 40%, thanks to their higher COP values, often exceeding 4.0.
You might also encounter cascade systems, which use two refrigerants for different temperature cycles, enhancing overall efficiency based on geographic conditions. By selecting the right type of heat pump, you can harness renewable energy effectively while ensuring ideal heating performance in your green building.
Factors Affecting Efficiency

The efficiency of heat pumps can fluctuate based on several factors, impacting their overall performance and energy consumption. One major consideration is the type of heat pump you choose. Air-source heat pumps (ASHPs) can show coefficient of performance (COP) values ranging from 1.8 to 5.0 in heating mode, while ground-source heat pumps (GSHPs) typically achieve COPs between 3.05 and 3.44. This makes GSHPs particularly advantageous in colder climates, where they can deliver up to 70% better heating efficiency due to stable underground temperatures.
Additionally, understanding the importance of effective treatment of depression in maintaining mental health can enhance your overall well-being while maximizing energy consumption in your green building.
Ambient conditions, like condenser inlet and outlet temperatures, also play a vital role in determining efficiency. The design and control strategy of your heat pump system can further enhance energy consumption, as the ideal operating points depend on the specific components and working fluids involved.
Additionally, variations in soil type and moisture levels can greatly affect GSHP performance in different geographic locations. Understanding these factors will help you make informed decisions that maximize the efficiency of your heat pump system, ensuring you get the best performance and energy savings in your green building.
Comparative Analysis of Case Studies

A comparative analysis of case studies reveals considerable insights into the efficiency of heat pumps in green buildings across different climates.
You'll find that air-source heat pumps (ASHP) often struggle in colder regions compared to ground-source heat pumps (GSHP), which maintain stable underground temperatures. For instance, in Saint Petersburg, the ASHP has a coefficient of performance (COP) of 2.357, while the GSHP boasts a COP of 2.44, showcasing its superior heat transfer efficiency.
Additionally, effective weight loss strategies can improve the overall performance of building occupants by encouraging healthier lifestyles, which may indirectly influence building energy use.
Further, GSHPs can provide remarkable energy savings, potentially lowering operational costs by up to 40% compared to traditional systems, which translates to a reduction of approximately 140 tons of CO2 emissions annually.
Numerous case studies highlight how optimized heat pump systems enhance the overall energy efficiency of green buildings, with reductions in home energy use ranging from 31% to 47%, depending on the efficiency ratings of the systems.
Additionally, research comparing local certification frameworks like Turkey's B.E.S.T. with LEED and BREEAM demonstrates that these frameworks can considerably improve energy management strategies in green buildings, optimizing resource consumption while ensuring occupant comfort.
Environmental and Economic Impacts

Optimizing heat pump systems not only enhances energy efficiency in green buildings but also yields significant environmental and economic benefits. By adopting heat pumps, you can reduce your home energy use by 31% to 47%, translating to economic savings on energy bills ranging from $300 to $650 annually. This shift contributes to a nationwide decline in greenhouse gas emissions, potentially reducing emissions in the residential sector by 36% to 64% when replacing fossil fuel heating systems.
| Impact Type | Benefits | Financial Aspects |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental | Reduced greenhouse gas emissions | Long-term savings offset installation costs |
| Economic | Significant energy cost reductions | Financial incentives available |
| System Type | Ground Source Heat Pumps outperforming traditional systems | Lifespan of over 50 years guarantees cost-effectiveness |
Ground Source Heat Pumps (GSHPs) achieve higher efficiency than traditional systems, improving heating efficiency by 70% and cooling efficiency by 20-40%. With financial incentives like those from the Inflation Reduction Act, the barriers of high installation costs diminish, making it easier for households to invest in renewable energy solutions that combat climate change and enhance the building sector.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is the Comparison Heat Pump Efficiency?
When comparing heat pump efficiency, you'll find air-source heat pumps (ASHPs) generally have lower performance in extreme cold, while ground-source heat pumps (GSHPs) offer higher efficiency and stability, especially in colder climates.
How Efficient Is a Heat Pump Compared to a Geothermal System?
Imagine cozying up in a warm blanket on a chilly day. When comparing heat pumps to geothermal systems, you'll find geothermal systems often shine brighter, especially in cold climates, delivering superior efficiency for your comfort needs.
What Is the Theoretical Efficiency of a Heat Pump?
The theoretical efficiency of a heat pump, measured by its Coefficient of Performance (COP), typically ranges from 1.8 to 5.0 in heating mode, depending on system type and operational conditions. You'll see significant variations.
How Do Heat Pumps Have Over 100% Efficiency?
Heat pumps achieve over 100% efficiency by transferring heat instead of generating it. You're utilizing energy from low-temperature sources, allowing you to move more energy than you consume, resulting in a coefficient of performance above one.
Conclusion
In the domain of green buildings, understanding heat pump efficiency is like finding the secret ingredient in a recipe—it's essential for peak performance. By exploring different systems and their influencing factors, you've seen how efficiency varies and impacts both the environment and your wallet. As you move forward, remember that the choices you make today can shape a sustainable tomorrow, ensuring that your building not only thrives but also contributes positively to the world around you.
-

 Residential and Commercial Applications4 months ago
Residential and Commercial Applications4 months agoBest Amana Heat Pump Reviews
-

 Thermal Energy Transfer4 months ago
Thermal Energy Transfer4 months agoBreakthroughs in Modern Heat Pump Systems: Thermal Energy Edition
-

 Residential and Commercial Applications4 months ago
Residential and Commercial Applications4 months agoBest Heat Pump
-

 Geothermal Heat Pumps3 months ago
Geothermal Heat Pumps3 months agoUpgrade Your Comfort with Our Efficient HVAC Systems
-

 Geothermal Heat Pumps3 months ago
Geothermal Heat Pumps3 months agoInnovative Geothermal Heat Pump Manufacturers Revolutionize Energy Efficiency
-

 Air Conditioning2 months ago
Air Conditioning2 months agoExploring Energy-Efficient Air Conditioning Heat Pumps
-

 Thermal Energy Transfer1 month ago
Thermal Energy Transfer1 month agoBoost Your Heat Pump Efficiency: Interactive Guide
-

 Air Conditioning4 months ago
Air Conditioning4 months agoHeat Pumps Outperform Traditional Heating in Energy Use











