Energy Consumption
Why Heat Pumps Excel at Thermal Energy Transfer

Here’s our rationale for considering heat pumps as outstanding in the realm of thermal energy transfer. They effectively transport warmth from one location to another, rendering them a perfect selection for either warming or cooling areas.
With key components and the use of refrigerants, heat pumps are able to transfer heat effectively.
We’ll explore the factors that affect thermal energy transfer and advancements in heat pump technology.
Join us as we delve into the world of heat pumps and their remarkable performance in serving your thermal needs.
Key Takeaways
- Heat pumps transfer thermal energy from one location to another by extracting heat from a low-temperature source and transferring it to a higher-temperature destination.
- Heat pumps have diverse applications in various industries and are commonly used in residential and commercial buildings for both heating and cooling purposes.
- Essential components of a heat pump system include the evaporator, compressor, condenser, and expansion valve, which work together to facilitate the transfer of thermal energy.
- Heat pumps are known for their high efficiency in transferring thermal energy, offering significant energy savings, lower environmental impact, and the ability to be powered by renewable energy sources.
The Basics of Thermal Energy Transfer
We will now explore the fundamentals of thermal energy transfer. Understanding the basics of energy transfer and the principles of heat transfer is crucial in comprehending how heat pumps excel at thermal energy transfer.
Energy transfer occurs through three main mechanisms: conduction, convection, and radiation. Conduction refers to the transfer of heat through direct contact between objects or substances. Convection involves the movement of heat through a fluid medium, such as air or water. Radiation is the transfer of heat through electromagnetic waves.
These principles are essential for understanding how heat pumps operate and transfer thermal energy efficiently. By comprehending these fundamentals, we can delve deeper into understanding heat pumps and their function, which we’ll explore in the subsequent section.
Understanding Heat Pumps and Their Function
Heat pumps function by transferring thermal energy from one location to another. They’re highly efficient devices that can be used for both heating and cooling purposes. Heat pumps work by extracting heat from a low-temperature source (such as air, water, or the ground) and transferring it to a higher-temperature destination. This process is achieved through the use of refrigerants and a series of key components, which we’ll discuss in the subsequent section.
Heat pumps have diverse applications in various industries. They’re commonly used in residential and commercial buildings for space heating and cooling. Additionally, heat pumps are utilized in industrial processes, such as food processing and chemical manufacturing, where precise temperature control is crucial. Proper maintenance is essential to ensure the optimal performance of heat pumps. Regular inspection, cleaning, and lubrication of the system components, as well as checking and replacing filters, are important heat pump maintenance tips to keep in mind.
In the next section, we’ll delve into the key components of a heat pump system and their roles in the thermal energy transfer process.
Key Components of a Heat Pump System
When it comes to understanding the key components of a heat pump system, there are several essential parts that work together to ensure efficient thermal energy transfer.
These components include the evaporator, compressor, condenser, and expansion valve.

The evaporator is responsible for absorbing heat from the surrounding environment, while the compressor increases the temperature and pressure of the refrigerant.
The condenser then releases the heat to the desired location, and the expansion valve controls the flow and pressure of the refrigerant.
Essential Heat Pump Parts
One of the most important parts of a heat pump system is the compressor. It plays a vital role in the heat transfer process by compressing the refrigerant and increasing its temperature.
Here are some other essential parts of a heat pump system:
Evaporator Coil: This component allows the refrigerant to absorb heat from the surrounding air or ground, depending on the type of heat pump.
Condenser Coil: The condenser coil releases heat from the refrigerant into the indoor or outdoor environment, depending on whether the system is in heating or cooling mode.
Expansion Valve: This valve regulates the flow of refrigerant, allowing it to expand and cool down before entering the evaporator coil.
Reversing Valve: In a heat pump, the reversing valve is responsible for reversing the flow of refrigerant, enabling the system to switch between heating and cooling modes.

Understanding these key components is crucial for heat pump maintenance and troubleshooting heat pump issues. By ensuring these parts are functioning properly, you can optimize the efficiency and performance of your heat pump system.
Function of Each Component
Understanding the function of each component is essential for optimizing the efficiency and performance of our heat pump system. A heat pump system consists of several key components that work together to transfer thermal energy. These components include the evaporator, compressor, and condenser.
The evaporator is responsible for absorbing heat from the surrounding environment, such as the air or ground. It utilizes a refrigerant to facilitate the heat transfer process. The compressor then increases the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant, which allows it to release the absorbed heat. Finally, the condenser releases the heat into the desired space, such as a home or building.
To ensure proper functioning of the heat pump system, regular heat pump maintenance is crucial. This includes cleaning or replacing filters, checking refrigerant levels, and inspecting electrical connections. In case of any issues, troubleshooting heat pump problems promptly can prevent further damage and ensure efficient operation. By understanding the function of each component and performing necessary maintenance, we can maximize the performance and longevity of our heat pump system.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Evaporator | Absorbs heat from the surrounding environment using a refrigerant |
| Compressor | Increases the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant |
| Condenser | Releases the absorbed heat into the desired space |
The Role of Refrigerants in Thermal Energy Transfer
As we delve into the role of refrigerants in thermal energy transfer, it becomes evident that they play a crucial part in the efficiency and effectiveness of heat pumps. Here are four key points to consider:
Refrigerant types: Different heat pump systems use different types of refrigerants, such as hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs), and natural refrigerants like ammonia or carbon dioxide. Each type has its own unique properties and environmental impact.
Environmental regulations: Due to concerns about their contribution to global warming and ozone depletion, many countries have implemented regulations to phase out the use of certain refrigerants, particularly those with high global warming potential. This has led to the development of more environmentally friendly alternatives.
Heat transfer properties: Refrigerants are chosen based on their ability to efficiently absorb and release thermal energy during the heat pump cycle. Their specific heat capacity, boiling point, and pressure-temperature relationship all play a role in maximizing heat transfer.

System optimization: The selection of the right refrigerant for a heat pump system is crucial for achieving optimal performance. Factors like operating conditions, system size, and environmental considerations must be taken into account to ensure efficient and reliable thermal energy transfer.
Efficiency and Performance of Heat Pumps
When it comes to heat pumps, one of the key factors that makes them stand out is their energy savings potential. Heat pumps are known for their high efficiency in transferring thermal energy, which translates to lower energy consumption and reduced utility bills.
Additionally, heat pumps have a lower environmental impact compared to traditional heating and cooling systems, as they rely on renewable energy sources such as air, water, or the ground.
However, it’s important to note that the performance of heat pumps can be influenced by various factors, including temperature extremes, equipment sizing, and proper maintenance.
Energy Savings Potential
We frequently achieve significant energy savings with heat pumps due to their efficient performance. Heat pumps offer a range of benefits that contribute to energy consumption reduction and cost effectiveness. Here are some key advantages:
High Efficiency: Heat pumps are designed to transfer heat rather than generate it, making them more energy-efficient than traditional heating systems.
Renewable Energy Integration: Heat pumps can be powered by renewable energy sources such as solar or geothermal, further reducing carbon footprint and dependency on fossil fuels.
Dual Functionality: Heat pumps can both heat and cool a space, eliminating the need for separate heating and cooling systems and reducing energy consumption.

Smart Controls: Advanced heat pump systems come with smart controls that allow users to optimize energy usage, schedule heating and cooling cycles, and monitor energy efficiency.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Our goal is to compare the environmental impact of heat pumps in terms of their efficiency and performance to determine their overall sustainability.
When it comes to environmental benefits, heat pumps are a clear winner. They operate by transferring heat from one place to another, rather than generating heat through combustion, which significantly reduces greenhouse gas emissions.
Additionally, heat pumps have a higher coefficient of performance (COP) compared to traditional heating and cooling systems, meaning they require less energy input to produce the same amount of heat or cooling output. This results in lower energy consumption and reduced reliance on fossil fuels.
To determine the overall sustainability of heat pumps, a comprehensive lifecycle analysis is necessary. This analysis should consider factors such as manufacturing, installation, operation, and end-of-life disposal.
Factors Affecting Performance
To achieve optimal efficiency and performance, heat pumps rely on various factors such as proper sizing, regular maintenance, and suitable operating conditions.
Improper installation can significantly affect the performance of a heat pump, leading to reduced efficiency and increased energy consumption. It’s crucial to ensure that the heat pump is correctly sized for the space it will serve, as an undersized system will struggle to meet the heating or cooling demands, while an oversized one will cycle on and off frequently, wasting energy.
Regular maintenance is also essential to keep the heat pump operating at its peak efficiency. This includes cleaning or replacing filters, checking refrigerant levels, and inspecting electrical connections. Heat pumps have specific maintenance requirements that should be followed to ensure optimal performance and longevity.

Factors Affecting Thermal Energy Transfer in Heat Pumps
Typically, several factors influence the efficiency of thermal energy transfer in heat pumps. These factors can include the type and condition of the heat pump, the temperature difference between the heat source and the heat sink, and the thermal energy storage capacity of the system.
To better understand these factors, let’s take a look at the following table:
| Factors | Description |
|---|---|
| Heat Pump Type | Different types of heat pumps have varying efficiencies. |
| Heat Pump Condition | Regular maintenance and proper functioning are crucial for efficiency. |
| Temperature Difference | A larger temperature difference generally leads to higher efficiency. |
| Thermal Energy Storage | The ability of the system to store and release thermal energy affects efficiency. |
Advancements in Heat Pump Technology
We have seen significant advancements in heat pump technology, and these advancements have greatly improved their efficiency and performance. Some of the key improvements in heat pump efficiency include:
Enhanced heat exchangers: New heat exchanger designs allow for more efficient transfer of thermal energy, resulting in better overall performance.

Variable speed compressors: These advanced compressors can adjust their speed based on the heating or cooling demands, leading to improved energy efficiency.
Smart controls: The integration of smart controls allows heat pumps to optimize their operation based on factors such as weather conditions and occupancy, further increasing efficiency.
Improved refrigerants: The use of environmentally friendly refrigerants with higher heat transfer capabilities has also contributed to the enhanced efficiency of heat pumps.
Looking ahead, future advancements in heat pump technology hold even more promise. Ongoing research and development efforts aim to further increase efficiency, reduce energy consumption, and improve overall performance, making heat pumps an even more attractive option for serving the energy needs of individuals and communities.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are Heat Pumps Suitable for All Types of Buildings and Climates?
Heat pumps have limitations in certain climates and building types. However, they can be suitable for many buildings and climates due to their energy efficiency. Consider factors like insulation and sizing for optimal performance.
How Does the Size of a Heat Pump Affect Its Efficiency?
The size of a heat pump directly affects its efficiency. When a heat pump is properly sized for a building, it can efficiently transfer thermal energy, resulting in optimal performance and energy savings.
Can Heat Pumps Be Used for Both Heating and Cooling Purposes?
Yes, heat pumps can be used for both heating and cooling purposes. Heat pump technology advancements have made it possible to transfer thermal energy efficiently, resulting in energy savings and improved comfort for users.
What Are the Environmental Benefits of Using a Heat Pump?
Using a heat pump offers significant environmental benefits. We can achieve high energy efficiency while reducing costs. This technology allows us to transfer thermal energy effectively, resulting in a more sustainable and eco-friendly solution.
Are There Any Government Incentives or Rebates Available for Installing a Heat Pump System?
There are government incentives and rebates available for heat pump installation. These programs aim to promote energy efficiency and reduce carbon emissions. They can help offset the initial costs and make heat pump systems more affordable for consumers.
What Advanced Techniques are Used to Revolutionize Heat Pump Technology?
The integration of smart controls, digitalization, and variable speed technology is revolutionizing heat pump technology. By optimizing performance, these advanced techniques enhance energy efficiency, reduce operating costs, and improve overall comfort levels. Revolutionizing heat pump technology allows for greater precision and adaptability, making them a more sustainable and reliable solution for heating and cooling needs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, heat pumps are exceptional at transferring thermal energy due to their efficient and innovative design. By utilizing refrigerants and key components, they’re able to effectively extract heat from one source and transfer it to another, providing both heating and cooling solutions.
With advancements in technology, heat pumps continue to improve in efficiency and performance, making them an ideal choice for sustainable and cost-effective thermal energy transfer.
Energy Consumption
Astonishing Contrast: Heat Pump Vs Traditional Heating

Upon first glance, traditional heating methods may seem like the obvious choice. But we urge you to reassess this perspective and let us introduce you to an unconventional alternative: the heat pump.
In this article, we will compare the efficiency, cost, environmental impact, installation process, performance, and more, of heat pumps and traditional heating systems. By exploring these aspects, we aim to shed light on the astonishing contrast between the two and help you make an informed decision that serves your needs and the environment.
Key Takeaways
- Heat pumps are highly efficient and consume less energy compared to traditional heating systems, resulting in substantial savings on utility bills.
- Heat pumps have a minimal environmental impact as they reduce carbon emissions and rely on renewable energy sources.
- Installation and maintenance costs of heat pumps are generally lower compared to traditional heating systems.
- Heat pumps provide efficient heating and cooling capabilities, are more reliable and cost-effective in the long run, and can be used year-round.
Efficiency Comparison: Heat Pump Vs Traditional Heating
We can compare the efficiency of a heat pump versus traditional heating systems. When it comes to cost effectiveness, heat pumps have a clear advantage. They’re highly efficient, utilizing renewable energy sources such as air, water, or the ground to transfer heat into or out of a building. This means that they consume less energy to produce the same amount of heat, resulting in lower utility bills for homeowners.
Additionally, heat pumps have a minimal environmental impact compared to traditional heating systems. By relying on renewable energy, they reduce carbon emissions and help mitigate climate change.
In the subsequent section about ‘cost analysis: heat pump vs traditional heating’, we’ll delve further into the financial benefits of heat pumps and how they compare to conventional heating methods.
Cost Analysis: Heat Pump Vs Traditional Heating
When considering the cost analysis of heat pump vs traditional heating, two key points come to mind: efficiency and energy savings, and installation and maintenance costs.
Heat pumps are known for their energy efficiency, which can result in significant savings on utility bills.
Additionally, the installation and maintenance costs of heat pumps are generally lower compared to traditional heating systems, making them a cost-effective choice in the long run.
Efficiency and Energy Savings
Our cost analysis reveals that the heat pump offers greater efficiency and energy savings compared to traditional heating methods.
Here are three key reasons why:
Cost Effectiveness: Heat pumps use a small amount of electricity to transfer heat from the outdoor air or ground into your home, making them significantly more energy-efficient than traditional heating systems. This results in lower energy bills and long-term cost savings.
Environmental Impact: Heat pumps produce less carbon emissions compared to traditional heating methods, reducing your carbon footprint and contributing to a greener environment. By using renewable energy sources like air or ground heat, heat pumps help to conserve natural resources and promote sustainability.

Energy Savings: Heat pumps utilize advanced technology to efficiently extract and distribute heat, resulting in higher energy efficiency ratings. This means that you can enjoy a comfortable indoor environment while consuming less energy, leading to substantial savings on your utility bills.
With these advantages in mind, let’s now explore the installation and maintenance costs of heat pumps.
Installation and Maintenance Costs
The installation and maintenance costs of a heat pump can be compared to those of traditional heating methods in terms of affordability and long-term savings. When considering the installation time, heat pumps generally take longer to install compared to traditional heating systems. This is because heat pumps require additional components such as the outdoor unit and refrigerant lines. However, the energy consumption of heat pumps is significantly lower, resulting in long-term savings on energy bills.
To further understand the cost analysis, let’s compare the installation and maintenance costs of a heat pump and a traditional heating system:

| Cost | Heat Pump | Traditional Heating |
|---|---|---|
| Installation Cost | $X | $Y |
| Maintenance Cost | $Z | $W |
| Total Cost (10 years) | $A | $B |
The installation and maintenance costs of heat pumps may be higher initially, but the energy savings over time can offset these costs, leading to substantial long-term savings.
Environmental Impact: Heat Pump Vs Traditional Heating
Using a heat pump for heating instead of traditional methods significantly reduces our carbon footprint. Here are three reasons why:
Lower Energy Consumption: Heat pumps are highly efficient in converting energy into heat. Unlike traditional heating systems that burn fossil fuels, heat pumps transfer heat from the air or ground, requiring less energy to produce the same amount of heat. This results in reduced greenhouse gas emissions and a smaller carbon footprint.
Renewable Energy Compatibility: Heat pumps can be powered by renewable energy sources such as solar or wind power. By utilizing clean energy, we further minimize our environmental impact and contribute to a sustainable future.

Reduced Emissions: Traditional heating methods release harmful pollutants into the atmosphere, contributing to air pollution and climate change. Heat pumps produce zero direct emissions, making them an environmentally friendly choice that helps protect our planet and public health.
Installation Process: Heat Pump Vs Traditional Heating
During the installation process, we can choose between a heat pump and traditional heating methods, but it’s important to consider the differences and advantages of each option.
When it comes to efficiency benefits, heat pumps have a clear advantage. They can transfer heat from the outside air or ground to warm the interior of a building, using minimal energy. This results in significant energy savings and reduced utility bills. Additionally, heat pumps can also be used for cooling during the summer, providing a versatile solution.
However, it’s important to note that heat pump installation can come with its own challenges. Proper sizing and placement of the unit, as well as the need for adequate insulation and ventilation, are crucial for optimal performance.
Traditional heating methods, on the other hand, may have simpler installation requirements but lack the energy efficiency benefits of heat pumps.
Performance and Reliability: Heat Pump Vs Traditional Heating
When comparing the performance and reliability of heat pumps and traditional heating systems, there are several key points to consider.
Firstly, the energy efficiency of heat pumps is significantly higher compared to traditional heating methods, resulting in lower energy consumption and reduced utility bills.
Secondly, heat pumps have a longer lifespan and require less maintenance compared to traditional heating systems, making them a more reliable and cost-effective option in the long run.
These points highlight the superior performance and reliability of heat pumps over traditional heating methods.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
In our comparison of energy efficiency, we discovered remarkable differences between the performance and reliability of heat pumps and traditional heating systems.
When it comes to cost effectiveness, heat pumps have a clear advantage. They’re highly efficient and can provide up to 4 units of heat for every 1 unit of electricity used. In contrast, traditional heating systems typically have an efficiency of 80% or lower.
In terms of environmental impact, heat pumps are also superior. They produce no greenhouse gas emissions on site and can be powered by renewable energy sources. On the other hand, traditional heating systems rely on fossil fuels, contributing to air pollution and climate change. These stark differences in energy efficiency make heat pumps a more sustainable and environmentally friendly choice.

Moving forward, let’s now delve into the topic of lifespan and maintenance.
Lifespan and Maintenance
We frequently find that heat pumps require less maintenance and have a longer lifespan compared to traditional heating systems. Heat pumps typically last around 15 to 20 years, while traditional heating systems have a lifespan of about 10 to 15 years. This means that heat pumps can provide reliable heating for a longer period of time, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
In terms of maintenance requirements, heat pumps require minimal maintenance compared to traditional heating systems. Regular filter cleaning and occasional servicing are usually sufficient to keep heat pumps running smoothly. In contrast, traditional heating systems often require more frequent maintenance, such as cleaning and replacing filters, as well as periodic inspections and repairs.
Maintenance and Upkeep: Heat Pump Vs Traditional Heating
Our heat pump requires regular maintenance every six months to ensure optimal performance and efficiency, while traditional heating systems typically only need annual upkeep. This is because heat pumps have more components that need to be checked and cleaned regularly, such as the evaporator coil, air filters, and refrigerant levels.
On the other hand, traditional heating systems, like furnaces or boilers, have simpler designs and fewer moving parts, which means they require less frequent maintenance.
However, it’s important to note that even though heat pumps need more frequent maintenance, they tend to have lower energy consumption compared to traditional heating systems. Additionally, regular maintenance can help identify and address any potential issues early on, reducing the risk of costly repairs down the line.
Noise Levels: Heat Pump Vs Traditional Heating
When comparing the noise levels of heat pumps and traditional heating systems, it becomes clear that the heat pump offers a significant advantage in terms of quietness.
The noise comparison between the two reveals that heat pumps operate at a much lower decibel level, resulting in a quieter and more peaceful environment.
This quietness factor is a key benefit of heat pumps and can greatly enhance the comfort and enjoyment of a living or working space.
Noise Comparison: Pump Vs. Traditional
The noise levels of a heat pump compared to traditional heating systems can be quite astonishing. When it comes to soundproofing options for both types of systems, it’s important to consider customer satisfaction.
Here are three key points to consider when comparing the noise levels of a heat pump and traditional heating:
Heat Pump: Heat pumps are known for their quieter operation compared to traditional heating systems. With advanced technology and sound-dampening features, heat pumps produce minimal noise during operation. This results in a more comfortable and peaceful environment for customers.

Traditional Heating: Traditional heating systems, such as furnaces or boilers, tend to generate more noise during operation. This can be attributed to the combustion process and the movement of air or water through the system. Customers may find the noise levels of traditional heating systems to be more intrusive and disruptive.
Soundproofing Options: For customers who are particularly sensitive to noise, soundproofing options can be employed for both heat pumps and traditional heating systems. This can include insulation, acoustic barriers, or sound-absorbing materials that help reduce the noise transmitted from the system into the living space.
Quietness Factor: Heat Pump
One important factor to consider when comparing the noise levels of a heat pump and traditional heating systems is the significant difference in quietness. Heat pumps operate with a remarkably low noise level, making them an ideal choice for those who desire a quiet and peaceful environment.
Unlike traditional heating systems, which can produce loud and disruptive sounds, heat pumps are designed to operate quietly. This is achieved through advanced soundproofing options and noise reduction techniques. The components of a heat pump, such as the compressor and fan, are engineered to minimize vibrations and reduce noise. Additionally, sound-absorbing materials are utilized to further dampen any potential noise.

Heating Capacity: Heat Pump Vs Traditional Heating
We can compare the heating capacity of a heat pump and traditional heating systems.
When it comes to heating performance, heat pumps offer excellent efficiency. They can extract heat from the environment and transfer it inside, providing a reliable source of warmth.
Traditional heating systems, on the other hand, rely on burning fuel or electricity to generate heat, which may not be as efficient.
In terms of energy consumption, heat pumps are known for their low energy usage. They can deliver more heat for every unit of energy consumed compared to traditional heating systems. This means that heat pumps can provide significant energy savings, resulting in lower utility bills for homeowners.
Adaptability and Flexibility: Heat Pump Vs Traditional Heating
We can compare the adaptability and flexibility of heat pumps and traditional heating systems.
Heat pumps offer a range of adaptability benefits and provide flexible heating options. One of the key advantages of heat pumps is their ability to provide both heating and cooling, making them suitable for year-round use. They can extract heat from the outdoor air or ground and transfer it inside during the colder months. In warmer weather, they can reverse the process and remove heat from indoor spaces, effectively cooling them.
This adaptability allows heat pumps to provide efficient heating and cooling solutions in a variety of climates. Additionally, heat pumps can be used in conjunction with existing heating systems, providing a flexible option for homeowners who want to supplement their traditional heating system with a more energy-efficient alternative.
Long-Term Savings: Heat Pump Vs Traditional Heating
Comparing the long-term savings between heat pumps and traditional heating systems reveals the significant cost advantages of using a heat pump. Here are three key reasons why heat pumps are more cost-effective in the long run:
Lower Energy Consumption: Heat pumps are highly efficient, utilizing renewable energy sources such as the air, ground, or water to transfer heat. Compared to traditional heating systems that rely on burning fuel, heat pumps consume less energy, resulting in reduced utility bills.
Reduced Maintenance and Repair Costs: Heat pumps have fewer moving parts and require less maintenance than traditional heating systems. With proper care and regular servicing, the risk of breakdowns and costly repairs is significantly lower.
Shorter Payback Period: Although heat pumps may have a higher upfront cost, their energy efficiency and lower operating expenses lead to a shorter payback period. The savings from reduced energy consumption and maintenance costs can quickly outweigh the initial investment, providing long-term financial benefits.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can a Heat Pump Be Used as a Standalone Heating System Without a Traditional Heating System?
Yes, a heat pump can function as a standalone heating system without the need for a traditional heating system. It is capable of efficiently providing heat by extracting warmth from the air or ground, making it a reliable and cost-effective option for standalone heating.
How Does the Efficiency of a Heat Pump Change in Extremely Cold Climates?
In extremely cold climates, the efficiency of a heat pump decreases due to the impact of temperature on its performance. This reduction in efficiency can lead to higher energy consumption and decreased heating capacity.
Are There Any Government Incentives or Rebates Available for Installing a Heat Pump?
Yes, there are government incentives and rebates available for heat pump installation. These programs aim to promote energy efficiency and reduce carbon emissions. It is important to check with local authorities for specific eligibility criteria and application procedures.
What Are the Potential Health Benefits of Using a Heat Pump Compared to Traditional Heating Methods?
Using a heat pump for heating can potentially provide health benefits compared to traditional methods. In addition to potential energy savings and a reduced environmental impact, heat pumps can improve indoor air quality and help prevent the spread of allergens and pollutants.
Can a Heat Pump Be Easily Integrated With Existing HVAC Systems?
Integrating a heat pump with existing HVAC systems is a seamless process. It provides efficient standalone heating, especially in cold climates. Plus, there are government incentives available and notable health benefits compared to traditional heating methods.

What Are the Differences Between a Heat Pump and Traditional Heating System?
Heat pumps vs traditional heating: While traditional heating systems generate heat by burning fuel or electricity, heat pumps transfer heat from one place to another using refrigerant. Heat pumps can provide both heating and cooling, making them versatile. They are energy-efficient and environmentally friendly, as they do not release any emissions. Traditional systems, on the other hand, may be simpler and cheaper to install but can be less efficient and more expensive to operate in the long run.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the comparison between heat pumps and traditional heating systems reveals astonishing contrasts. Heat pumps offer higher efficiency, lower operating costs, and reduced environmental impact. The installation process is straightforward, and their performance and reliability are commendable.
Additionally, heat pumps operate quietly and have a flexible adaptability to different heating needs. With their long-term savings potential, it’s clear that heat pumps are a superior choice for heating needs, providing both comfort and efficiency.
Energy Consumption
Curated Guide: Slash Energy Consumption With Heat Pumps

- Real life examples: successful energy reduction with heat pumps
- Challenges and solutions: implementing heat pumps for energy reduction
Welcome to our meticulously chosen guide on reducing energy usage with heat pumps. We have gathered the most valuable information to help you make informed decisions and decrease your energy consumption.
Discover the benefits of heat pumps, learn how they work, and find the right one for your home or business.
With our tips on installation, maintenance, and energy-saving strategies, you’ll be on your way to achieving impressive efficiency and cost savings.
Prepare to be inspired by real-life case studies showcasing successful energy reduction with heat pumps.
Key Takeaways
- Heat pumps are an energy-efficient and environmentally friendly option for heating and cooling homes.
- They can reduce energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions by up to 50% compared to other heating systems.
- Heat pumps can provide both heating and cooling, eliminating the need for separate air conditioning systems.
- Proper installation, maintenance, and choosing the right model based on climate conditions are crucial for optimal heat pump performance.
The Benefits of Heat Pumps
We love heat pumps because they help us save energy and reduce our carbon footprint. Heat pump installation is an effective way to lower energy consumption and decrease greenhouse gas emissions. Compared to traditional heating and cooling systems, heat pumps can provide significant energy savings. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, heat pumps can reduce electricity use for heating by up to 50%.
Additionally, heat pumps can also provide cooling during warmer months, eliminating the need for separate air conditioning systems. However, it’s important to consider the drawbacks of heat pumps. They can be more expensive to install compared to conventional systems, and their efficiency can be affected by extreme temperatures.
Nevertheless, the long-term energy savings and environmental benefits make heat pumps an attractive option for reducing our impact on the planet.
How Heat Pumps Work
Let’s start by understanding the basics of how heat pumps work. Heat pumps are highly efficient devices that transfer heat from one place to another, using a small amount of energy. This means they can provide both heating and cooling for your home, making them versatile and cost-effective.
Additionally, heat pumps have the added benefit of reducing environmental impact by lowering carbon emissions compared to traditional heating systems.
Heat Pump Basics
Understanding how heat pumps work can help us make informed decisions about our energy consumption. Here are four key aspects of heat pump basics:
Heat Transfer: Heat pumps use a refrigerant to transfer heat from one area to another, providing both heating and cooling capabilities.
Reversible Operation: Heat pumps can be reversed to provide either heating or cooling, making them versatile for year-round comfort.
Efficiency: Heat pumps are highly efficient, as they transfer heat rather than generating it, resulting in significant energy savings compared to traditional heating and cooling systems.
Maintenance and Installation: Proper heat pump maintenance and installation are crucial for optimal performance and longevity. Regular inspections, filter cleaning, and professional servicing ensure efficient operation and prevent breakdowns.
Understanding these heat pump basics empowers us to make smart choices regarding installation, maintenance, and energy consumption, ultimately reducing our environmental impact.
Energy Efficiency Benefits
By understanding the energy efficiency benefits of heat pumps, we can maximize our savings and minimize our environmental impact.
Heat pumps are energy saving techniques that work by transferring heat from one place to another. Unlike traditional heating systems that generate heat, heat pumps extract heat from the air, ground, or water, and then distribute it throughout a building. This process requires less energy compared to generating heat from scratch.
Heat pumps are also energy efficient appliances because they can produce up to three times more heat energy than the electrical energy they consume. In fact, studies have shown that heat pumps can reduce energy consumption by 30-60% compared to other heating systems.
Environmental Impact Reduction
While heat pumps are effective in reducing energy consumption, they also have a significant positive impact on the environment. Here are four reasons why heat pumps contribute to environmental impact reduction:
Energy Efficiency: Heat pumps are one of the most energy-saving techniques available today. They can provide up to four times more energy than they consume, making them highly efficient in heating and cooling spaces.

Reduced Carbon Emissions: Heat pumps rely on renewable energy sources, such as the air or ground, to transfer heat. This eliminates the need for burning fossil fuels, resulting in lower carbon emissions and reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
Ozone Layer Protection: Unlike traditional heating systems, heat pumps don’t emit harmful gases that contribute to ozone layer depletion. By using heat pumps, we can help protect the ozone layer and prevent further environmental damage.
Reduced Air Pollution: Heat pumps produce cleaner air by eliminating the combustion process associated with traditional heating methods. This helps to improve air quality and reduce pollution, creating a healthier environment for all.
Types of Heat Pumps
We will explore three main types of heat pumps that can help reduce energy consumption in our homes.
The first type is geothermal heat pumps, which extract heat from the ground and transfer it into our homes. These pumps are highly efficient and can provide both heating and cooling.
The second type is air source heat pumps, which extract heat from the air and transfer it into our homes. These pumps are more common and affordable than geothermal heat pumps, but they’re also less efficient.
Lastly, there are hybrid heat pumps that combine the benefits of both geothermal and air source heat pumps. These pumps automatically switch between the two heat sources depending on the outdoor temperature.
Choosing the right heat pump for your home or business is crucial in maximizing energy savings and reducing environmental impact.

Choosing the Right Heat Pump for Your Home or Business
Our main consideration when choosing a heat pump for our home or business should be its efficiency and capacity to meet our heating and cooling needs. To ensure we make the right choice, we should take into account the following factors:
Heat pump sizing: It’s crucial to select a heat pump that’s appropriately sized for our space. A system that’s too small will struggle to keep our home or business comfortable, while one that’s too large will cycle on and off frequently, leading to energy waste.
Cost considerations: We need to weigh the upfront cost of purchasing and installing a heat pump against the potential long-term energy savings. Additionally, it’s essential to consider maintenance and repair costs to ensure our investment remains cost-effective over time.
Energy efficiency ratings: Look for heat pumps with high Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) and Heating Seasonal Performance Factor (HSPF) ratings. The higher these ratings, the more energy-efficient the heat pump will be, resulting in lower energy costs.

Climate compatibility: Consider the climate in which our home or business is located. Heat pumps have different performance characteristics in varying temperatures, so it’s crucial to choose a model that’s suitable for our specific climate conditions.
Installation and Maintenance Tips for Heat Pumps
When it comes to heat pumps, proper installation techniques are crucial for optimal performance and energy efficiency.
Regular maintenance is also key to ensure the longevity and effectiveness of the system.
Additionally, implementing energy-efficient operation tips can further reduce energy consumption and save on utility costs.
Proper Installation Techniques
Let’s ensure a successful installation of your heat pump by following proper techniques and maintenance tips. Here are some common installation mistakes to avoid:
Size matters: Ensure that your heat pump is properly sized for your space. An undersized unit will struggle to meet your heating and cooling needs, while an oversized one may cycle on and off frequently, wasting energy.
Proper placement: Choose an optimal location for your heat pump that allows for efficient airflow and minimizes obstructions. Avoid placing it near sources of heat or cold that may interfere with its performance.
Correct refrigerant charge: Improper refrigerant levels can lead to reduced efficiency and even system failure. Make sure the refrigerant charge is accurately measured and adjusted during installation.

Professional installation: While DIY may be tempting, it’s crucial to hire a qualified professional for heat pump installation. They have the expertise to ensure all components are properly connected and calibrated for optimal performance.
Regular Maintenance Requirements
We can ensure optimal performance and efficiency of our heat pumps by regularly maintaining them and following proper installation and maintenance tips. Regular maintenance is essential to prevent common issues and keep the heat pump running smoothly. Here is a suggested regular maintenance schedule for your heat pump:
| Maintenance Task | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Clean or Replace Air Filters | Every 1-3 months |
| Check and Clean Outdoor Unit | Every 6-12 months |
| Inspect and Clean Ducts | Every 1-2 years |
| Lubricate Moving Parts | Every 1-2 years |
| Schedule Professional Check-up | Annually |
Energy-Efficient Operation Tips
How can we ensure energy-efficient operation of our heat pumps through proper installation and maintenance tips?
Here are four energy-saving techniques that can help reduce your carbon footprint:
Proper installation: Ensure that your heat pump is installed correctly by a qualified professional. This includes proper sizing, placement, and insulation to maximize efficiency.
Regular maintenance: Schedule regular maintenance checks to ensure your heat pump is running at peak performance. This includes cleaning or replacing filters, checking refrigerant levels, and inspecting electrical connections.
Temperature settings: Set your heat pump at optimal temperature settings. Lowering the thermostat by a few degrees in winter and raising it in summer can significantly reduce energy consumption.
Smart controls: Consider installing smart controls or programmable thermostats to optimize your heat pump’s efficiency. These devices allow you to schedule temperature adjustments based on your daily routines, saving energy when you’re not at home.

Energy-Saving Tips With Heat Pumps
We can maximize energy efficiency by optimizing the settings on our heat pumps. By utilizing the energy-saving benefits of heat pump technology advancements, we can significantly reduce our energy consumption and save on utility bills.
One important tip is to set the thermostat to the most efficient temperature, typically between 18 to 20 degrees Celsius for heating and 24 to 26 degrees Celsius for cooling. It’s also recommended to use the timer or programmable thermostat feature to adjust the temperature based on our daily schedule.
Regularly cleaning and maintaining the heat pump is essential to ensure optimal performance.
Heat Pump Efficiency and Cost Savings
By implementing energy-efficient heat pumps, homeowners can achieve significant cost savings on their utility bills. Here are four key factors that contribute to heat pump efficiency and cost savings:
Proper heat pump maintenance: Regular maintenance, such as cleaning or replacing air filters, ensures optimal performance and energy efficiency. It also helps prevent breakdowns and extends the lifespan of the heat pump.
Energy-saving strategies: Using programmable thermostats, sealing air leaks, and improving insulation can further enhance heat pump efficiency. These strategies minimize energy waste and reduce overall heating and cooling costs.
Seasonal efficiency ratings: When purchasing a heat pump, look for high Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) and Heating Seasonal Performance Factor (HSPF) ratings. Higher ratings indicate better energy efficiency and potential cost savings.
Professional installation: Hiring a qualified technician to install your heat pump ensures proper sizing and installation. This maximizes efficiency and reduces energy consumption, leading to long-term cost savings.

Case Studies: Successful Energy Reduction With Heat Pumps
In our research, we’ve found several case studies that demonstrate successful energy reduction with heat pumps. These real-life examples showcase the effectiveness of heat pumps in slashing energy consumption.
One case study involved a commercial building in a busy city center. By implementing heat pumps for both heating and cooling, the building achieved a remarkable 40% reduction in energy usage.
Another case study focused on a residential complex. By replacing traditional HVAC systems with heat pumps, the complex reduced its energy consumption by 30%.
These success stories highlight the potential of heat pumps in achieving substantial energy savings.
However, implementing heat pumps for energy reduction does come with challenges. These include upfront costs, retrofitting existing systems, and ensuring proper sizing and installation.
However, with careful planning and consideration of these challenges, the benefits of heat pumps can be fully realized.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Heat Pumps Be Used in Commercial Buildings as Well as Residential Homes?
Yes, heat pumps can be used in commercial buildings as well as residential homes. They offer significant energy efficiency benefits in large scale applications, reducing both costs and environmental impact.
How Long Does a Heat Pump Typically Last Before Needing to Be Replaced?
Heat pumps typically last around 10-15 years before needing replacement. Regular heat pump maintenance, like cleaning and checking for signs of failure, can help prolong its lifespan.

Are Heat Pumps Noisy When They Are Running?
Heat pump noise levels can vary, but there are best practices for reducing noise. Regular maintenance, proper installation, and locating the unit away from living spaces can help minimize any potential noise disruptions.
Can a Heat Pump Be Used as the Sole Source of Heating and Cooling in a Home or Business?
Yes, a heat pump can be used as the sole source of heating and cooling in a home or business. It offers high heat pump efficiency, reducing energy consumption and providing numerous benefits for users.
Are There Any Government Incentives or Rebates Available for Installing a Heat Pump?
There are government incentives and rebates available for installing a heat pump, which can help offset the cost. These incentives are designed to promote energy savings and encourage the use of more efficient heating and cooling systems.
Are Ground Source Heat Pumps Really Energy Guzzlers?
Ground source heat pumps unravel energy consumption by utilizing the constant temperature beneath the Earth’s surface to heat and cool buildings efficiently. Contrary to popular belief, these innovative systems are not energy guzzlers. By relying on renewable energy and converting it into usable heat, ground source heat pumps offer an eco-friendly alternative that can significantly reduce energy consumption and carbon emissions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, heat pumps offer numerous benefits in reducing energy consumption for homes and businesses.
Did you know that heat pumps can reduce heating and cooling costs by up to 50% compared to traditional HVAC systems?
With their efficient operation and versatility, heat pumps are a smart choice for anyone looking to slash energy consumption and save money in the long run.
Consider installing a heat pump to enjoy the benefits of lower energy bills and a more sustainable future.
Energy Consumption
5 Keys to Ground Source Heat Pump Efficiency

Looking to improve the efficiency of your ground source heat pump system? Look no further!
In this article, we will share with you the 5 key strategies that will help you achieve optimal performance.
From proper sizing and design to effective ground loop installation and maintenance, we’ve got you covered.
We’ll also delve into the benefits of energy-saving controls and smart thermostats, as well as provide you with valuable maintenance and troubleshooting tips.
Let’s dive in and start serving your efficiency needs!
Key Takeaways
- Proper sizing and design of ground source heat pump systems contribute to optimal efficiency.
- Effective ground loop installation and maintenance are crucial for efficient heat transfer and system performance.
- Utilizing energy-saving controls and smart thermostats enhances the efficiency of ground source heat pump systems.
- Regular system maintenance and troubleshooting are essential for ensuring efficient performance and addressing potential issues.
Understanding the Benefits of Ground Source Heat Pump Systems
We’re excited to explore the many benefits of ground source heat pump systems.
Ground source heat pumps, also known as geothermal heat pumps, offer numerous advantages for residential buildings. One of the main benefits is their ability to provide heating, cooling, and hot water, all from a single system. This can lead to significant energy savings and reduced utility bills.
Another advantage is the environmental impact. Ground source heat pumps use the earth’s natural heat, which is a renewable energy source, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and lowering greenhouse gas emissions.
Additionally, these systems have a long lifespan and require minimal maintenance, making them a cost-effective and sustainable choice for homeowners.
Proper Sizing and Design for Optimal Efficiency
Our team ensures that the proper sizing and design of ground source heat pump systems are implemented to achieve optimal efficiency. Here are four key factors we consider during the ground source heat pump installation process:
Heat load calculation: We accurately calculate the heating and cooling needs of your space to determine the appropriate size of the heat pump. This ensures that the system operates efficiently without wasting energy.
Ground loop design: We carefully design the ground loop system, taking into account factors such as soil type, available space, and thermal conductivity. This allows for efficient heat transfer between the ground and the heat pump.

Equipment selection: We recommend energy efficient heat pump models that are properly sized for your specific needs. This ensures optimal performance and reduces energy consumption.
Distribution system design: We design the distribution system, including ductwork or radiant heating, to ensure balanced airflow and efficient heat distribution throughout your space.
Effective Ground Loop Installation and Maintenance
To ensure optimal performance and longevity of the ground source heat pump system, our team focuses on effective installation and regular maintenance.
The ground loop design is a critical component of the system, as it determines the efficiency of heat transfer between the ground and the heat pump. Our team carefully considers factors such as soil type, depth, and thermal properties when designing the ground loop. This ensures maximum heat exchange and minimizes energy losses.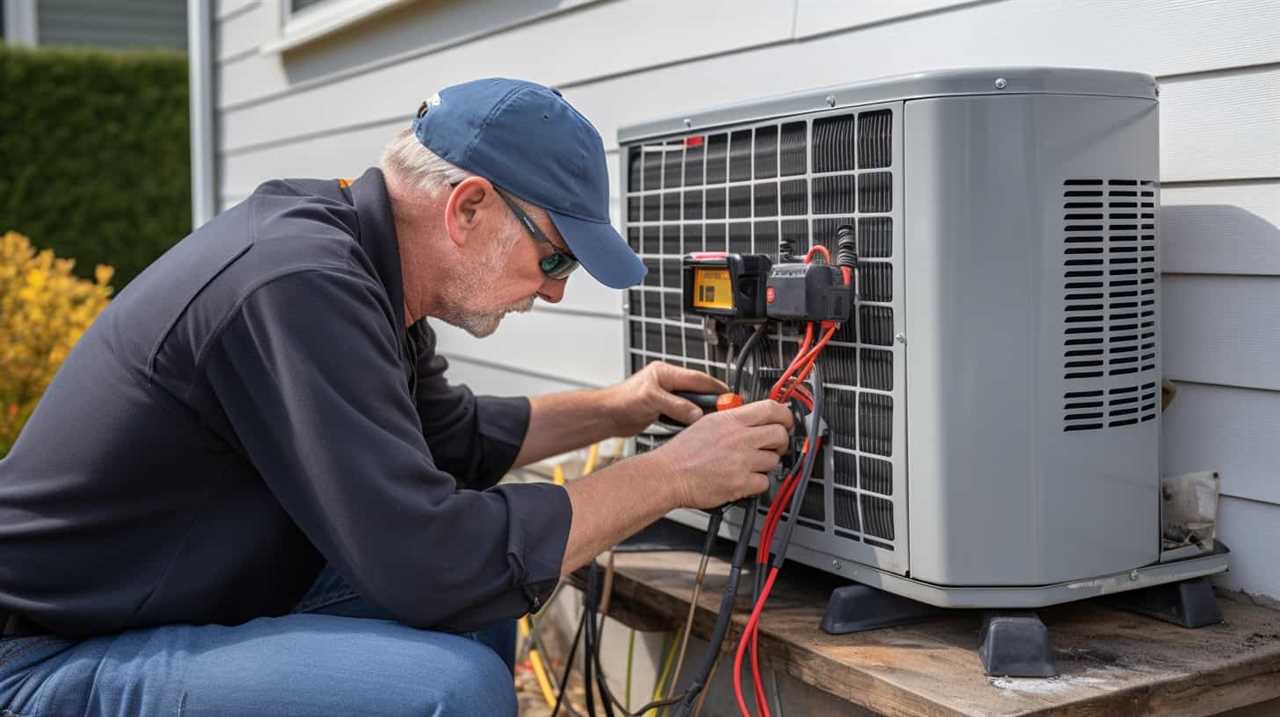
Additionally, proper installation techniques are employed to avoid any damage to the ground loop, such as leaks or improper connections.
Regular ground loop maintenance is also essential to maintain the system’s efficiency. Our team conducts periodic inspections, checks for leaks, and cleans the loop to ensure optimal performance.
Utilizing Energy-Saving Controls and Smart Thermostats
While utilizing energy-saving controls and smart thermostats, we can significantly enhance the efficiency of our ground source heat pump systems. Here are four ways energy management and cost savings can be achieved:
Programmable thermostats: By setting specific temperature schedules, we can optimize energy usage and reduce wasteful heating or cooling when not needed.

Occupancy sensors: These smart controls detect movement and adjust the temperature accordingly, ensuring comfortable conditions only when the space is occupied.
Remote access: With smart thermostats, we can control and monitor our heating and cooling systems from anywhere, allowing us to adjust settings based on our needs and save energy when we’re away.
Learning capabilities: Some smart thermostats can learn our preferences and automatically adjust settings to maximize comfort while minimizing energy consumption.
By implementing these energy-saving controls and smart thermostats, we can achieve significant cost savings and improve the overall efficiency of our ground source heat pump systems.
Now, let’s explore the importance of regular system maintenance and troubleshooting tips.
Regular System Maintenance and Troubleshooting Tips
Proper system maintenance and regular troubleshooting are essential for ensuring the efficient performance of our ground source heat pump systems. By following a systematic maintenance checklist, we can identify and address potential issues before they escalate, ensuring optimal system operation.
One important troubleshooting tip is to regularly check the system’s air filters and clean or replace them as needed. Clogged filters can restrict airflow, reducing the system’s efficiency.
Additionally, it’s crucial to inspect the heat pump’s coils and fins for any dirt or debris buildup, as this can hinder heat transfer.

Regularly monitoring the system’s refrigerant levels and ensuring that they’re within the manufacturer’s recommended range is also vital for efficient operation.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Much Does a Ground Source Heat Pump System Cost to Install?
Installing a ground source heat pump system involves various cost factors, such as the size of the property, ground conditions, and system complexity. The installation process typically includes drilling boreholes, laying underground pipes, and connecting the system to the property’s heating and cooling distribution system.
Are Ground Source Heat Pump Systems Eligible for Any Government Incentives or Rebates?
Government incentives and rebates can help offset the cost of installing a ground source heat pump system. These incentives vary by location and can provide a significant cost breakdown, making the system more affordable for homeowners.
Can a Ground Source Heat Pump System Be Installed in Any Type of Property, Such as a Residential Home or Commercial Building?
Yes, a ground source heat pump system can be installed in both residential homes and commercial buildings. There are pros and cons to consider for each type of installation, such as cost, space requirements, and energy savings potential.
Are There Any Limitations or Restrictions on the Depth or Length of the Ground Loop for a Ground Source Heat Pump System?
There are some depth limitations and length restrictions to consider when installing a ground source heat pump system. These factors can impact the efficiency and performance of the system.
How Long Does It Typically Take to Recoup the Initial Investment of a Ground Source Heat Pump System Through Energy Savings?
Typically, it takes several years to recoup the initial investment of a ground source heat pump system through energy savings. However, the recouping period can vary depending on factors such as energy prices and system efficiency.
What are the Factors that Contribute to the Energy Efficiency of Ground Source Heat Pumps?
The energy efficiency of ground source heat pumps relies on multiple factors. Proper insulation, sizing, and design of the system contribute to ground source heat pumps’ efficiency. Ground heat exchangers, underground loops, and heat transfer efficiency within the system also play crucial roles in maximizing the performance of ground source heat pumps efficiency. Efficient functioning can lead to reduced energy consumption and lower heating and cooling costs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, optimizing the efficiency of ground source heat pump systems requires careful consideration of various factors. By understanding the benefits, properly sizing and designing the system, implementing effective ground loop installation and maintenance, utilizing energy-saving controls and smart thermostats, and performing regular system maintenance, homeowners can ensure optimal performance and energy savings.
It’s time to embrace these key practices and harness the full potential of ground source heat pumps, unlocking a sustainable and cost-effective heating and cooling solution for the future.
-

 Residential and Commercial Applications7 months ago
Residential and Commercial Applications7 months agoBest Amana Heat Pump Reviews
-

 Thermal Energy Transfer7 months ago
Thermal Energy Transfer7 months agoBreakthroughs in Modern Heat Pump Systems: Thermal Energy Edition
-

 Geothermal Heat Pumps6 months ago
Geothermal Heat Pumps6 months agoInnovative Geothermal Heat Pump Manufacturers Revolutionize Energy Efficiency
-

 Residential and Commercial Applications7 months ago
Residential and Commercial Applications7 months agoBest Heat Pump
-

 Geothermal Heat Pumps6 months ago
Geothermal Heat Pumps6 months agoUpgrade Your Comfort with Our Efficient HVAC Systems
-

 Air Conditioning5 months ago
Air Conditioning5 months agoExploring Energy-Efficient Air Conditioning Heat Pumps
-

 Energy Consumption3 months ago
Energy Consumption3 months ago10 Key Comparisons: Heat Pump Vs Traditional Heating
-

 Thermal Energy Transfer4 months ago
Thermal Energy Transfer4 months agoBoost Your Heat Pump Efficiency: Interactive Guide








