When choosing between heat pumps and traditional boilers, consider efficiency, environmental impact, and upfront costs. Heat pumps use less energy, produce fewer emissions, and are easier to install and maintain, making them ideal for milder climates. Boilers, while less expensive initially and better for colder areas, tend to have higher ongoing costs and more maintenance. To understand which option suits your home best and how to make an informed decision, explore the details further.
Key Takeaways
- Heat pumps offer higher efficiency and lower operating costs, especially in moderate climates, compared to traditional boilers.
- Traditional boilers can perform better in extremely cold weather but generally have higher fuel or energy expenses.
- Heat pumps are easier to install, occupy less space, and often include smart thermostat compatibility.
- Boilers require more maintenance, have shorter lifespans, and involve higher ongoing costs.
- Environmentally, heat pumps emit fewer greenhouse gases and support renewable energy use, making them more eco-friendly.

Rheem 50 Gal. Smart High Efficiency Hybrid Heat Pump Water Heater with 10-Year Warranty
It must be wired into your home’s electrical system and will typically require a dedicated electrical circuit (similar…
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Overview of Heating Systems: Boilers and Heat Pumps

Heating systems come in various forms, but two of the most common are traditional boilers and modern heat pumps. Boilers heat water, then distribute it through radiators or underfloor systems to warm your home. They often use thermostat control to maintain a set temperature, but zoning systems are less common with boilers, making it harder to customize heating in different areas. Heat pumps, on the other hand, extract heat from the outside air or ground and are highly efficient. They often feature advanced thermostat control, allowing precise temperature adjustments. Additionally, zoning systems are more compatible with heat pumps, enabling you to heat specific areas independently. Both systems have their benefits, but understanding their control options helps you decide which suits your home’s needs best. Heat pump efficiency can significantly influence long-term energy savings and environmental impact.
best traditional boilers for cold climates
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
How Traditional Boilers Operate

Traditional boilers heat water by burning fuel, creating a combustion process that releases heat. This hot water then circulates through radiators or pipes to warm your space. You’ll also need to maintain the system regularly to guarantee safe operation and efficiency. Incorporating exfoliation benefits can enhance overall system performance and longevity.
Combustion Process Explained
To produce heat, a boiler burns fuel—usually natural gas, oil, or coal—in a controlled combustion process. This combustion converts fuel into heat energy, which heats water in the system. The efficiency of this process depends on combustion efficiency, which measures how well the fuel’s energy is converted into usable heat. Different fuel types influence how efficiently the boiler operates; natural gas generally offers higher efficiency and cleaner combustion, while oil and coal may produce more emissions and require different handling. The combustion process involves mixing fuel with air and igniting it to generate heat. Proper control of this process guarantees maximum efficiency and safety, minimizing waste and emissions. The heat generated then transfers to the water, ready for distribution through your heating system. Additionally, maintaining optimal combustion conditions is essential for reducing emissions and ensuring environmental compliance.
Heat Distribution Methods
Once the boiler generates heat through combustion, it needs an effective way to distribute that warmth throughout your building. Traditional boilers use various heat distribution methods, including:
- Radiator Types – from classic cast iron to modern panel radiators, these devices emit heat into rooms efficiently.
- Underfloor Systems – these circulate hot water beneath floors, providing even, comfortable warmth.
- Pipe Networks – interconnected pipes carry hot water or steam to radiators or underfloor systems, ensuring consistent heating.
Each method impacts comfort and efficiency. Radiators focus heat in specific areas, while underfloor systems deliver a more uniform temperature. Choosing the right heat distribution method depends on your home’s layout and your heating preferences.
System Maintenance Needs
Maintaining a traditional boiler requires regular attention to guarantee it operates safely and efficiently. You should routinely check and replace filters to prevent dirt buildup that can hinder performance. Regular filter replacement helps keep the system running smoothly and reduces the risk of breakdowns. Additionally, system troubleshooting is essential when you notice unusual noises, inconsistent heating, or increased energy bills. Diagnosing issues early can prevent costly repairs and extend the boiler’s lifespan. Keep an eye on pressure levels and listen for leaks or unusual sounds, which may indicate underlying problems. Scheduling annual professional inspections ensures your boiler remains in good working order, addressing minor issues before they escalate. Proper maintenance not only enhances efficiency but also ensures your home stays warm and safe all winter long. Incorporating system maintenance practices can help identify potential problems early and keep your heating system operating at optimal performance.

New! Honeywell Home Smart Thermostat, Conventional/Heat Pump Compatibility, WiFi Thermostat for Home, X2S, Gray
CONTROL: Connect to WiFi and control from anywhere using the First Alert app – Matter Certified and also…
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
The Mechanism Behind Heat Pumps

Heat pumps work by transferring heat from one place to another rather than generating it directly, making them highly efficient for heating and cooling. This process relies on thermodynamic principles and a refrigeration cycle that moves heat instead of producing it. When operating, the heat pump absorbs heat from the outside air, ground, or water, then compresses the refrigerant to increase its temperature. The hot refrigerant releases heat inside your home. Here’s how it works:
- Absorption of heat from the environment using the refrigeration cycle.
- Compression of refrigerant to boost temperature.
- Heat transfer to your home’s interior through a heat exchanger.
This cycle allows heat pumps to provide efficient, eco-friendly heating by redistributing existing heat rather than creating new heat. Additionally, understanding the importance of personality traits can help improve interactions with installation technicians and service providers.

Water Heating Solutions: Tankless, Heat Pump, and Solar Systems That Slash Your Second-Largest Expense (The Sustainable Home Energy Series)
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Cost Comparison: Initial Investment and Long-term Expenses
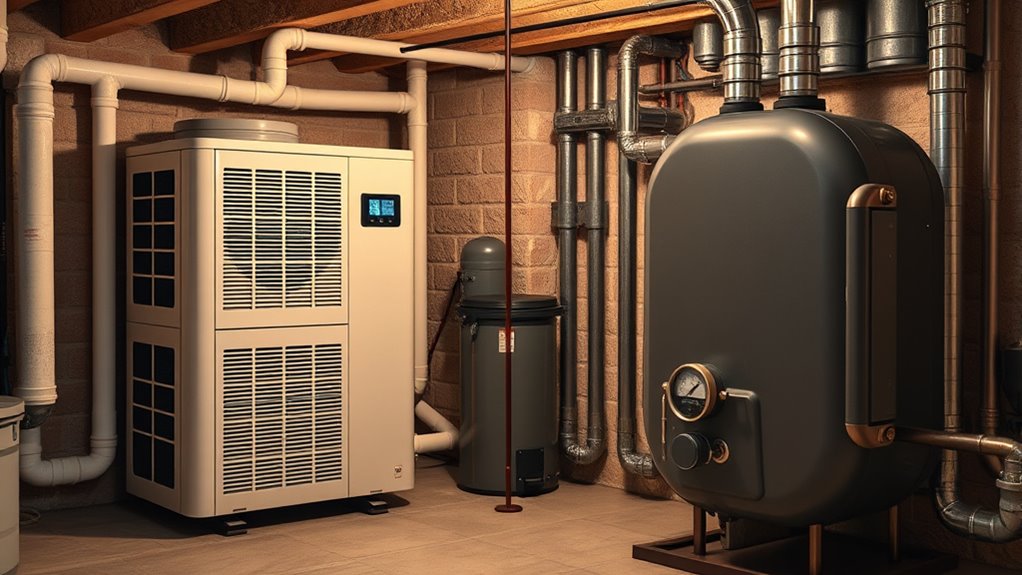
While heat pumps often have higher upfront costs than traditional boilers, their long-term expenses can be more economical. The initial investment for a heat pump typically includes higher upfront costs due to advanced technology and installation requirements. However, these costs are offset over time by lower recurring expenses, since heat pumps operate more efficiently and use less energy. Traditional boilers usually have lower initial costs but can lead to higher ongoing expenses because of increased fuel or electricity consumption. Over the lifespan of the system, the savings from reduced energy bills can outweigh the initial price difference. Additionally, energy efficiency plays a crucial role in determining overall cost savings and environmental impact. When comparing costs, it’s important to contemplate both the upfront investment and the recurring expenses to determine which heating system offers better long-term value.
Energy Efficiency and Operational Costs

When it comes to ongoing costs, energy efficiency plays a key role in choosing between heat pumps and traditional boilers. Heat pumps generally use less energy because they transfer heat rather than generate it, saving you money over time. Here are three key points:
- They can reduce your utility bills by up to 50%, especially if you access renewable sources of energy.
- Lower operational costs stem from higher efficiency, which means less fuel consumption regardless of fluctuating utility rates.
- Traditional boilers tend to be less efficient, especially in colder climates, leading to higher expenses as they rely more on fossil fuels.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability

Choosing between heat pumps and traditional boilers substantially impacts your home’s environmental footprint. Heat pumps generally have a lower carbon footprint because they rely on electricity, which can come from renewable energy sources. This means they produce fewer greenhouse gases during operation, helping combat climate change. Traditional boilers, especially those fueled by fossil fuels like natural gas or oil, emit more carbon dioxide and other pollutants, increasing your home’s overall environmental impact. By opting for a heat pump, you support cleaner energy use and reduce reliance on non-renewable resources. While both systems have sustainability considerations, heat pumps tend to be more environmentally friendly over their lifespan, contributing to a greener, more sustainable future for your home and the planet. Additionally, energy efficiency of heat pumps plays a significant role in reducing overall emissions and conserving resources.
Installation Processes and Space Requirements

Installing a heat pump is generally more straightforward and less invasive than setting up a traditional boiler, especially with modern, compact models designed for easy integration. Heat pumps typically require minimal ductwork adjustments, making installation quicker. They also have a smaller space footprint, fitting into closets or small utility rooms without much hassle. Additionally, heat pumps often incorporate advanced climate control features that enhance efficiency and comfort during operation.
Maintenance and Longevity

Compared to traditional boilers, heat pumps generally require less ongoing maintenance, thanks to their simpler design and fewer moving parts. This simplicity enhances system durability, making heat pumps less prone to wear and tear. As a result, you’ll likely experience a lower repair frequency over time. Regular checks of filters and refrigerant levels are typically sufficient to keep the system running efficiently. Unlike boilers, which may need frequent repairs due to complex components like burners and valves, heat pumps tend to be more reliable. This reduced need for repairs not only saves you money but also minimizes downtime. Additionally, the use of vetted first home theatre projectors ensures optimal performance and longevity of the system. Overall, heat pumps offer a longer lifespan and less maintenance hassle, making them a durable and convenient choice for home heating.
Making the Right Choice for Your Home

To select the optimal system for your home, consider both the initial costs and ongoing efficiency. Think about how installation and maintenance fit into your budget and lifestyle. Making an informed decision guarantees you get reliable heating that saves you money in the long run. Additionally, exploring options like Mazda Tuning can provide insights into customizing performance and efficiency features for different vehicle types, which parallels the importance of tailoring home heating solutions to your specific needs.
Cost and Efficiency
Choosing between heat pumps and traditional boilers largely depends on their costs and efficiency, which can substantially impact your long-term expenses. Here are key points to weigh:
- Upfront costs vary: heat pumps usually require a higher initial investment but can lead to greater energy savings over time.
- Energy efficiency: heat pumps are more efficient in moderate climates, reducing your monthly bills, while boilers may be more effective in colder regions.
- Long-term savings: despite higher upfront costs, heat pumps often lower operating expenses due to their superior efficiency, making them a smart choice for cost-conscious homeowners.
Ultimately, understanding these factors helps you choose a system that balances initial investment with ongoing savings.
Installation and Maintenance
When considering installation and maintenance, it’s important to recognize that each system has different requirements that can affect your long-term convenience and costs. Heat pumps, especially ductless systems, are typically easier and quicker to install, often needing less invasive work. They also work well with smart thermostats, allowing you to optimize energy use effortlessly. Maintenance for heat pumps usually involves annual inspections and filter changes, which are straightforward. Traditional boilers, on the other hand, may require more extensive setup, such as ductwork or chimney considerations, and maintenance can be more involved, including boiler servicing and potential repairs. While both systems benefit from routine upkeep, ductless heat pumps with smart thermostats tend to offer simpler, more flexible maintenance, making them a convenient choice for many homeowners.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which Heating System Has a Longer Lifespan?
When comparing the lifespan of heating systems, you’ll find that traditional boilers generally have a longer durability comparison, often lasting 15-30 years with proper maintenance. Heat pumps tend to have a shorter lifespan, around 10-15 years, due to more complex components. Maintenance requirements also differ; boilers usually need less frequent upkeep, while heat pumps require regular checks to ensure efficiency. Your choice depends on long-term durability and ongoing maintenance needs.
Can Heat Pumps Work Effectively in Extremely Cold Climates?
Ever wonder if your heat pump can handle a cold climate? You might worry about efficiency concerns when temperatures plummet. The truth is, modern cold climate heat pumps are designed to work effectively even in freezing weather, but their efficiency can drop as it gets colder. So, yes, they can operate in cold climates, but you should consider models built specifically for low temperatures to guarantee reliable warmth.
Are There Government Incentives for Installing Heat Pumps or Boilers?
You can often find government incentives like grants and tax credits to help cover installation costs. These programs aim to encourage energy-efficient upgrades, so check your local, state, or federal resources. By taking advantage of government grants or tax credits, you reduce your upfront expenses and make eco-friendly choices more affordable. Always verify eligibility and application deadlines to maximize your savings when installing heat pumps or boilers.
How Do Noise Levels Compare Between Heat Pumps and Boilers?
You’ll find noise levels vary between heat pumps and boilers. Heat pumps generally produce more sound during operation, especially outside units, but good sound insulation can minimize disruption. Boilers tend to be quieter, with less noise from combustion or movement. If noise is a concern, consider installing sound insulation around the units or choosing models designed for quieter operation, helping you enjoy a peaceful home environment.
What Are the Potential Future Technological Advancements in Home Heating Systems?
You might worry about outdated home heating systems, but future advancements will revolutionize your comfort and efficiency. Expect smarter systems integrating with the smart grid, enabling real-time energy management. Innovations will increase renewable energy compatibility, reducing emissions and costs. Enhanced controls, AI-driven optimization, and improved insulation materials will make home heating more sustainable, reliable, and cost-effective, ensuring you stay comfortable while supporting a greener future.
Conclusion
Choosing between a heat pump and a traditional boiler is like picking between a trusty old car and a sleek electric one—you’ll want what fits your journey best. Think of heat pumps as the eco-friendly breeze guiding your home’s warmth with whispering efficiency, while boilers are the dependable workhors you’ve known. Whichever you choose, making an informed decision is like planting a seed for a cozy, sustainable future—you’ll reap comfort and savings for years to come.









