Air-source heat pumps tend to use more energy during cold weather since they struggle to extract heat efficiently outside. In contrast, geothermal systems operate more consistently, thanks to stable underground temperatures, which makes them more energy-efficient year-round. While geothermal systems often have higher upfront costs, they save money over time through lower energy use and reduced environmental impact. To explore more about how these systems compare, keep exploring the details below.
Key Takeaways
- Geothermal systems generally consume less energy year-round due to stable underground temperatures.
- Air-source heat pumps are less efficient in extremely cold weather, increasing energy use during cold spells.
- Over time, geothermal systems typically require less electricity, reducing overall energy consumption.
- Rising energy prices make geothermal systems more cost-effective and energy-efficient long-term.
- Outdoor noise and environmental impact are lower with geothermal systems, indirectly influencing energy sustainability.
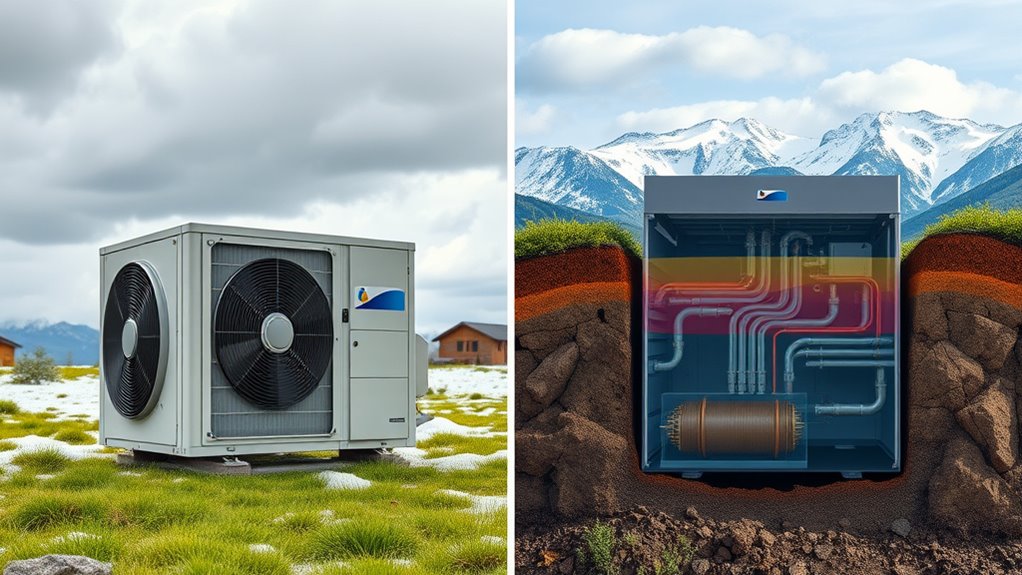
When comparing energy consumption between air-source and geothermal systems, understanding their efficiency is key. Both systems aim to heat and cool your home, but they do so in different ways, which markedly affects their cost efficiency and environmental impact. Air-source heat pumps extract heat from the outside air and transfer it inside during winter, and reverse the process in summer. While they’re generally less expensive to install initially, they tend to be less efficient in extremely cold climates, leading to higher energy use during cold spells. This increased consumption can raise your utility bills and reduce overall cost efficiency. On the other hand, geothermal systems leverage the stable temperatures beneath the earth’s surface, using underground loops filled with water or antifreeze. This constant temperature allows geothermal heat pumps to operate more efficiently year-round, using less energy to maintain comfortable indoor temperatures. As a result, geothermal systems often provide better cost efficiency over the long term, despite their higher upfront costs. The environmental impact of each system also varies appreciably. Air-source systems, while cleaner than traditional fossil fuel-based heating, still rely heavily on electricity, which may be generated from non-renewable sources. This reliance contributes to higher carbon emissions if your local grid isn’t powered by renewable energy. In contrast, geothermal systems are considered more environmentally friendly because they consume less electricity overall and have a smaller carbon footprint. Their ability to operate efficiently in diverse climates means you’re likely to generate fewer greenhouse gases over the system’s lifetime, making them a more sustainable choice. You’ll also notice that geothermal systems minimize outdoor noise because their components are mostly underground or indoors, reducing sound pollution. However, their environmental benefits are most pronounced when the electricity powering them comes from renewable sources. When evaluating your options, consider how the efficiency of each system impacts your long-term expenses and environmental footprint. Although geothermal systems require a larger initial investment, their lower energy consumption makes them more economical over time, especially if energy prices rise. Additionally, their reduced environmental impact aligns with sustainable living goals, making them an attractive option for eco-conscious homeowners. Overall, understanding the difference in energy consumption helps you make smarter choices that balance upfront costs with ongoing savings and ecological benefits. Both systems have their merits, but when prioritizing efficiency, environmental impact, and long-term savings, geothermal systems often come out ahead. By choosing wisely, you can enjoy a more cost-effective, environmentally friendly home climate control system that reduces your carbon footprint and lowers your energy bills in the long run.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does Climate Impact the Efficiency of Each System?
Climate variability markedly impacts each system’s efficiency. In colder climates, air-source heat pumps struggle with seasonal performance, requiring more energy to heat your home. Conversely, geothermal systems maintain consistent efficiency regardless of seasonal changes because they tap into stable underground temperatures. If you live in areas with extreme or fluctuating weather, a geothermal system may offer better energy savings and reliable performance year-round.
What Are the Long-Term Maintenance Costs for Both Systems?
You’ll find that long-term maintenance costs for both systems involve routine inspections and component replacements. Air-source systems generally have lower initial costs but may need more frequent repairs due to outdoor exposure. Geothermal systems tend to have higher upfront costs but benefit from fewer moving parts, which reduces maintenance over time. Overall, you should budget for regular checks and occasional replacements to keep both systems running efficiently.
Can Both Systems Be Integrated With Renewable Energy Sources?
Imagine your home basking in the glow of solar panels, seamlessly blending with your heating system. Yes, both air-source and geothermal systems can be integrated with renewable energy sources, creating hybrid systems that maximize efficiency. This renewable integration reduces reliance on fossil fuels, lowers energy bills, and boosts sustainability. By combining these technologies, you craft an eco-friendly solution that harnesses nature’s power while maintaining comfort year-round.
How Do Installation Costs Compare for Urban Versus Rural Settings?
In urban settings, installation costs tend to be higher due to installation challenges and complex urban infrastructure. You might face limited space, restricted access, and the need to navigate existing buildings and underground utilities. Conversely, in rural areas, installation is usually simpler and less expensive because of more available space and easier access. However, urban environments require careful planning, which can increase overall costs, making rural installations generally more cost-effective upfront.
Are There Any Government Incentives for Upgrading to Geothermal Systems?
Yes, you can benefit from government incentives when upgrading to geothermal systems. These incentives often include tax credits, rebates, or grants that make the upgrade benefits more affordable. By taking advantage of these programs, you lower your initial costs and enjoy long-term savings on energy bills. Check with local or federal agencies to see what’s available in your area, and consider how these incentives make geothermal systems a smart, eco-friendly choice.
Conclusion
Imagine choosing between a cautious, steady friend and an adventurous one; both get you where you need to go, but one might tire faster. Similarly, air-source systems are like the cautious friend—more susceptible to outside weather, leading to higher energy use. Geothermal systems, like the adventurous friend, rely on stable underground temperatures, making them more energy-efficient. If you want consistent comfort, investing in geothermal feels like having a reliable companion that saves energy in the long run.









