When comparing lifecycle costs, geothermal heat pumps typically have higher upfront expenses due to installation but benefit from lower maintenance, longer lifespan, and greater efficiency, which save you money over time. Air source systems cost less initially but may need more repairs and have shorter durability, resulting in higher long-term costs. Both systems can be improved with incentives and future tech upgrades. Keep exploring to find out how these factors impact your long-term savings and eco-friendliness.
Key Takeaways
- Geothermal systems have higher initial installation costs but lower long-term operating and maintenance expenses due to durability and efficiency.
- Air source heat pumps typically incur lower upfront costs but may face higher repair and energy costs over their 10-15 year lifespan.
- Geothermal systems last 20-25 years or more, reducing replacement frequency and associated costs compared to air source units.
- Both systems benefit from incentives that can offset initial investments, influencing overall lifecycle costs.
- Technological advancements are narrowing cost differences, making future upgrades and efficiency improvements relevant in lifecycle considerations.

Senville LETO Series Mini Split Air Conditioner Heat Pump, 12000 BTU 110/120V, Inverter, Works with Alexa, SEER2 20.8, 1 Ton, White
Alexa Enabled Mini Split AC/Heating System: Integrate with voice control or app, allowing you to adjust your mini...
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Initial Installation Expenses

When comparing the initial installation expenses of geothermal and air source heat pumps, geothermal systems typically cost more upfront because of the need for underground loops or boreholes. This means your installation costs are higher initially, requiring a significant upfront investment. The process involves excavating land or drilling deep into the ground, which adds to labor and material costs. In contrast, air source heat pumps are easier and quicker to install, resulting in lower initial expenses. While the upfront investment for geothermal systems is steeper, it often reflects the long-term savings and efficiency benefits they provide. So, if you’re considering installation costs, keep in mind that geothermal systems demand a larger initial outlay but may pay off over time. Additionally, self-serve options at some local shops make trying frozen yogurt more convenient and customizable.

DELLA Motto Series Mini Split AC, 208-230V 17.5 SEER2 Cools up to 550 Sq.Ft, 12000 BTU Air Conditioner & Heater with 1 Ton Pre-Charged Heat Pump, Works with Alexa and WiFi
QUIET OPERATION & INSTALLATION: This system mandates professional installation as it's not a DIY mini split AC. This...
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Long-Term Maintenance and Repairs

You’ll find that geothermal systems generally need less frequent maintenance than air source units, which require regular checks and filter changes. Repair costs can vary widely depending on the system’s complexity and age, influencing your long-term expenses. Both types differ in durability, with geothermal systems often lasting longer and requiring fewer repairs over their lifespan. Additionally, considering natural techniques for site preparation can reduce long-term maintenance needs by promoting healthier system operation.
Maintenance Frequency Differences
While both geothermal and air source heat pumps require regular maintenance to operate efficiently, geothermal systems generally demand less frequent repairs over their lifespan. This increased system reliability means fewer interruptions and greater user convenience. With geothermal systems, you typically experience:
- Longer intervals between service visits
- Fewer component failures due to protected underground loops
- Reduced wear on compressor parts, lowering overall repair needs
These factors make geothermal systems more dependable, decreasing the frequency of scheduled checks and unexpected repairs. As a result, you’ll enjoy a smoother operation with less hassle. The lower maintenance frequency not only boosts system reliability but also minimizes disruption, saving you time and money over the long term. Additionally, understanding the efficiency ratings can help optimize your system’s long-term performance.
Repair Costs Variability
Geothermal systems typically incur lower repair costs over their lifespan due to their robust design and protected underground components. However, repair costs can still fluctuate based on factors like regional pricing and specific system issues. Since geothermal units have fewer moving parts exposed to the environment, they’re less prone to damage, which helps keep costs stable. But when repairs are needed, regional pricing differences for labor and parts can cause some variation in expenses. Additionally, the complexity of certain repairs, such as ground loop repairs, may lead to higher costs in some areas. Overall, while geothermal systems tend to have more predictable and lower repair costs, understanding local cost fluctuations can help you better prepare for potential long-term maintenance expenses.
Longevity and Durability
Because geothermal heat pumps are built with fewer moving parts and are largely protected underground, they tend to last longer and require less frequent repairs compared to air source systems. Their superior corrosion resistance helps prevent rust and material degradation over time. High material quality ensures components withstand environmental stresses, reducing failures. You’ll benefit from fewer breakdowns and lower maintenance costs. Additionally, material durability contributes significantly to the system’s longevity and resilience. Key durability advantages include:
- Enhanced corrosion resistance due to underground placement
- Use of high-quality materials prolonging system life
- Fewer moving parts decreasing wear and tear
This means your geothermal system can operate effectively for 20-25 years or more, compared to the typical 10-15 years for air source units. The combination of corrosion resistance and material quality makes geothermal heat pumps a more durable, long-lasting choice.

MEPTY 9000BTU Mini Split AC/Heating System, 19 SEER2 Energy Efficient Mini Split Air Conditioner with Heat Pump, Cools Up to 450sq.ft, Ductless Inverter AC Unit with Pre-Charged Condenser
⭐Advanced Energy Saving: Advanced inverter technology with leading 19 SEER2 rating delivers superior performance through ensuring that the...
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Energy Efficiency and Operating Costs

When comparing energy efficiency and operating costs, geothermal heat pumps typically outperform air source heat pumps due to their stable underground temperature, which allows them to operate more efficiently year-round. This efficiency leads to lower energy bills and reduced long-term costs. However, reliability concerns may arise if the underground loops aren’t properly installed or maintained, potentially affecting performance. Aesthetic considerations also come into play; geothermal systems require ground or water source installation, which can impact your landscape’s appearance. In contrast, air source heat pumps are less invasive visually but tend to be less efficient in extreme weather, increasing operational costs during cold winters. Overall, geothermal systems offer better energy savings, but initial installation and aesthetic impacts are factors to weigh carefully. Additionally, advancements in AI-powered technology are beginning to influence the design and optimization of these systems, promising even greater efficiencies in the future.

12,000 BTU Mini Split AC & Heat Pump | 115v, Inverter, Smart WiFi, DIY Install, Remote | Ultra-Quiet, Energy Efficient for 750 Sq.Ft Space
Superior Cooling & Heating: Effectively cools and heats spaces up to 750 sq. ft. with 12,000 BTU inverter...
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Lifespan and Durability of Systems

The lifespan and durability of heat pump systems vary considerably between geothermal and air source models, impacting your long-term investment. Geothermal systems typically offer longer system component longevity thanks to buried loops protected from weather, while air source units face more wear from environmental exposure. Material durability also differs, with geothermal components built to withstand underground conditions, reducing corrosion risks. Key points include:
- Extended system component longevity of geothermal units, often exceeding 25 years.
- Enhanced material durability in geothermal parts, resistant to weather and environmental stressors.
- Shorter lifespan of air source heat pumps, generally around 10-15 years, due to exposure to elements.
- The use of specialized materials in geothermal systems further contributes to their resistance against corrosion and environmental degradation.
Understanding these differences helps you plan for maintenance and replacements, ensuring your system remains reliable over time.
Environmental Impact and Incentives

You can reduce your environmental footprint by choosing systems with lower emissions, and geothermal heat pumps typically outperform air source options in this regard. Incentive programs are available in many areas to help offset installation costs for both types of systems. Exploring these options can make a more sustainable and cost-effective choice easier for you. Additionally, geothermal systems utilize Earth’s natural heat, which is a renewable energy source, further reducing environmental impact.
Environmental Footprint Comparison
Have you ever wondered how geothermal and air source heat pumps compare regarding their environmental footprints? Geothermal systems generally have a lower impact because they rely on renewable energy from the earth’s stable heat. They considerably reduce carbon emissions over their lifetime, helping you cut your overall environmental footprint. Air source heat pumps, while efficient, depend more on electricity, which may come from fossil fuels, increasing their carbon footprint. Additionally, the high efficiency of geothermal systems often results in lower operational costs and fewer environmental impacts over time.
Key differences include:
- Geothermal systems use less electricity, decreasing carbon emissions
- They rely on renewable energy sources, making them more sustainable
- Air source heat pumps may produce higher emissions depending on grid energy sources
Choosing geothermal can be a smarter environmental choice, especially if you aim to minimize your impact on the planet.
Incentive Program Availability
Incentive programs can substantially influence your decision to install geothermal or air source heat pumps by reducing upfront costs and encouraging eco-friendly choices. Many governments offer rebates that directly lower installation expenses, making these systems more affordable. To access these benefits, you need to check program eligibility, which varies by location and specific requirements. Some programs prioritize renewable energy systems, while others may have income or property type restrictions. Staying informed about available government rebates can help you maximize savings and ensure you’re taking advantage of financial incentives designed to promote sustainable home upgrades. By understanding the incentive landscape, you can make a more cost-effective choice that aligns with your environmental goals and budget. Additionally, for sale 100, exploring local options can reveal unique programs tailored to your region’s environmental initiatives and incentives.
Resale Value and Home Investment Benefits

When considering home improvements, installing a geothermal or air source heat pump can substantially boost your property’s resale value. These systems appeal to buyers due to increasing market demand for energy-efficient homes and their aesthetic appeal. Adding such upgrades shows your commitment to sustainability, which many buyers prioritize. It can also differentiate your property in a competitive market, leading to higher offers. Benefits include:
- Enhanced energy efficiency attracting eco-conscious buyers
- Improved aesthetic appeal with sleek, modern equipment
- Increased market demand for homes with sustainable features
Investing in these systems not only reduces your ongoing costs but also makes your home more attractive to future buyers, delivering long-term home investment benefits. Embracing imagination in your home upgrades can inspire innovative solutions, further enhancing your property’s appeal and functionality.
Potential for Future Upgrades
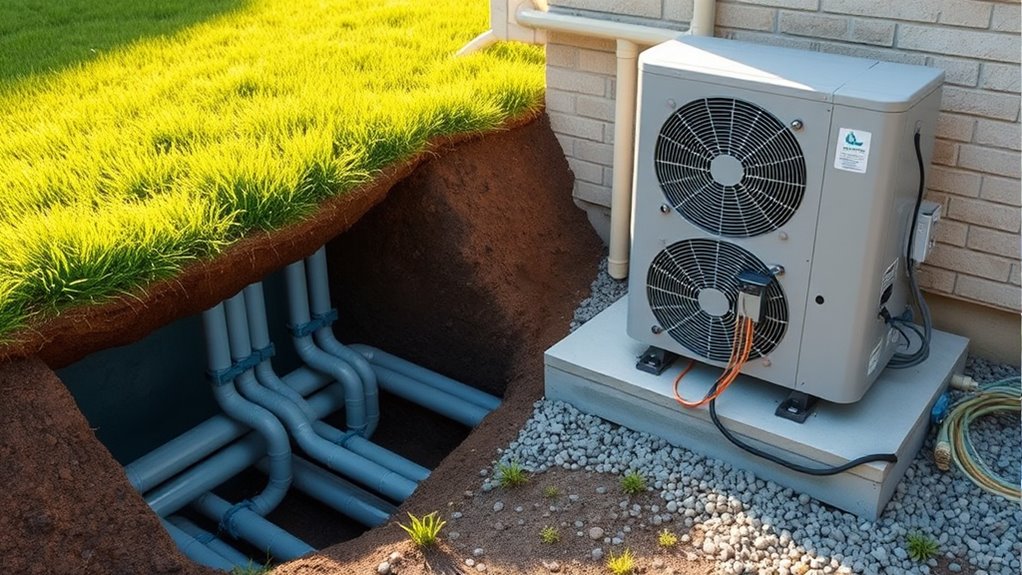
Upgrading to a geothermal or air source heat pump not only benefits your home today but also opens the door for future enhancements. Both systems have strong future upgrade potential, especially with advancements in technology integration. You can expand or enhance your system as new features emerge, such as smart controls or higher efficiency components. Visualize this potential with the following:
| Feature | Current State | Future Possibility |
|---|---|---|
| Smart technology | Basic thermostats | Fully integrated AI systems |
| Efficiency modules | Standard components | Modular upgrades for efficiency |
| Connectivity | Limited remote control | IoT-enabled management |
| Renewable integration | Basic geothermal or air source | Hybrid systems with solar |
This flexibility guarantees your investment remains adaptable and future-proof.
Overall Cost-Benefit Analysis

Have you considered how the long-term costs and benefits compare between geothermal and air source heat pumps? A thorough overall cost-benefit analysis reveals key differences. Geothermal systems tend to have higher upfront costs but offer stable operational expenses due to less impact from cost fluctuation and energy price changes. Technological advancements are making geothermal more efficient and affordable. Conversely, air source heat pumps often have lower initial costs and benefit from rapid improvements driven by innovation.
Geothermal offers stable costs despite higher upfront investment; air source heat pumps are more affordable initially but may have variable long-term expenses.
- Lower installation costs for air source pumps initially
- Geothermal’s stability reduces long-term financial risk
- Technological advancements are narrowing efficiency gaps
Ultimately, your decision depends on balancing upfront investment against ongoing savings, considering future technological developments and fluctuating energy prices.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do Local Climate Conditions Influence Geothermal vs. Air Source Heat Pump Costs?
Imagine your home as a tree, rooted in its environment. Climate impact is like the soil’s richness, shaping how well systems thrive. For geothermal, colder climates mean deeper, more costly drilling, increasing cost variability. Air source heat pumps, however, struggle in extreme cold, reducing efficiency. Your local climate directly influences installation and operating costs, making climate impact a crucial factor in choosing the right system, affecting long-term expenses.
What Are the Environmental Benefits Beyond Energy Savings for Each System?
When considering environmental benefits beyond energy savings, geothermal and air source heat pumps help reduce your carbon footprint, supporting recycling programs and wildlife conservation efforts. Geothermal systems have minimal land disturbance and long-lasting components, while air source units emit fewer greenhouse gases than traditional systems. Choosing either system promotes sustainable living, conserves natural resources, and encourages eco-friendly practices that benefit local ecosystems and community recycling initiatives.
How Do Installation Challenges Vary Between Geothermal and Air Source Options?
You might find installation challenges surprising; geothermal systems often demand extensive trenching, making installation complex and costly upfront. Conversely, air source heat pumps usually require less invasive installation, with simpler setup and minimal trenching. This difference means geothermal installation can be more disruptive and time-consuming, especially in tight spaces, while air source units offer quicker, less intrusive options. Your choice depends on your site’s landscape and your willingness to handle these installation complexities.
Are There Specific Home Types Better Suited for One System Over the Other?
You’ll find that home architecture and property size influence which heat pump suits you best. If your home has a traditional or compact design, an air source heat pump is easier to install and maintain. Larger properties or those with specific architectural features benefit from geothermal systems, as their ground loops require space and stable conditions. Consider your home’s layout and property size to choose the most efficient, suitable system.
What Financing Options Are Typically Available for Geothermal and Air Source Heat Pumps?
Think of financing options as a toolbox for your home’s energy upgrade. You can access financing incentives and loan programs that make installing geothermal or air source heat pumps more affordable. Many options include low-interest loans, rebates, and grants, helping you cut costs upfront. Check with local utilities or government programs to find tailored incentives, making your eco-friendly switch smoother and more budget-friendly.
Conclusion
Considering the lifecycle costs, geothermal heat pumps typically have a higher upfront price but lower long-term operating expenses—saving you around 40% on energy bills over 20 years. Air source systems may be cheaper initially but often require more maintenance and have shorter lifespans. With geothermal’s durability of 25+ years, you’ll enjoy better value and environmental benefits. Investing wisely now means enjoying significant savings and sustainability benefits for years to come.









