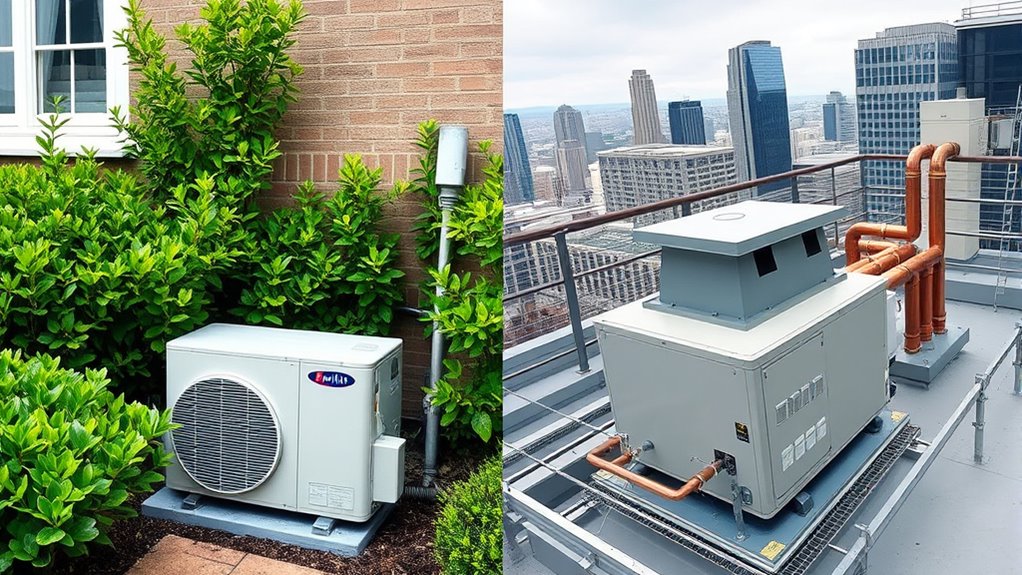
Residential heat pumps are designed for small spaces like homes or apartments, offering efficient heating and cooling with simpler installation and lower costs. Commercial systems handle larger areas such as offices or industrial facilities, with more complex technology, higher capacity, and increased operational costs. They include advanced controls to optimize performance. If you’re curious about how these systems compare regarding size, efficiency, and expense, you’ll find useful insights as you explore further.
Key Takeaways
- Residential heat pumps are designed for small spaces, while commercial systems handle larger, complex environments.
- Commercial units typically feature advanced control systems for performance optimization compared to simpler residential models.
- Installation of residential systems is straightforward and less costly; commercial setups involve complex procedures and higher costs.
- Residential systems emphasize energy efficiency for individual homes, whereas commercial units balance efficiency with larger-scale demands.
- Operational costs are generally lower for residential systems, but commercial systems can offer long-term savings through optimized performance.
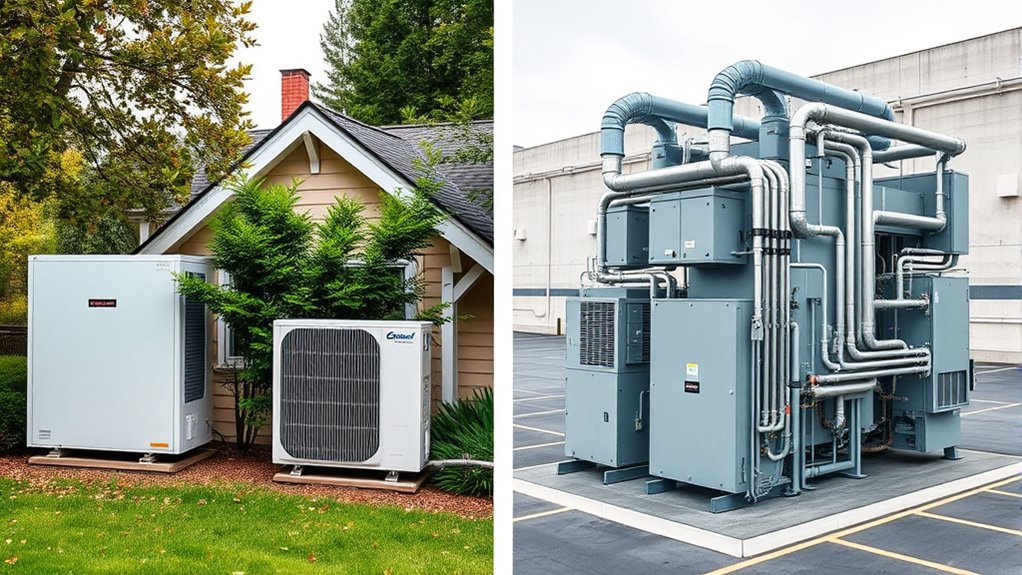
When choosing a heat pump system, understanding the differences between residential and commercial options is essential. One of the most important factors to contemplate is energy efficiency. Residential heat pumps are designed to meet the heating and cooling needs of a single-family home or small apartment. They typically operate efficiently within smaller spaces, using less energy overall. Because these systems are tailored for individual homes, they often incorporate advanced technology to maximize energy savings, which can lead to lower utility bills over time. Commercial heat pumps, on the other hand, are built to handle larger, more complex spaces like office buildings, retail centers, or industrial facilities. They need to maintain high energy efficiency across extensive areas, often requiring more powerful equipment and sophisticated control systems. While their energy efficiency can be high, the larger scale means they consume more power and may have higher operational costs, especially if not properly designed or maintained. Additionally, commercial systems often feature advanced control systems to optimize performance across large-scale environments.
Installation costs are another key difference. Residential heat pump installation is generally straightforward and less expensive because these systems are smaller and easier to fit into existing structures. You might find that installation costs are manageable, especially if your home already has compatible ductwork or electrical infrastructure. Conversely, commercial heat pumps usually demand more complex installation procedures. They often involve significant modifications to the building’s electrical systems, ductwork, or even structural elements. These systems are larger and require specialized expertise, which drives up installation costs considerably. In addition, commercial projects may include permits, engineering assessments, and longer installation timelines, further contributing to higher upfront expenses. While the initial investment for commercial heat pumps can be substantial, their ability to serve large spaces efficiently can result in long-term savings through reduced energy consumption.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do Maintenance Needs Differ Between Residential and Commercial Heat Pumps?
You’ll find that maintenance needs differ mainly in frequency and scope. Commercial heat pumps require more frequent maintenance due to higher usage, meaning filter replacement and system checks happen more often. Residential systems usually need less frequent attention, often just seasonal filter replacements and routine inspections. By staying on top of these maintenance tasks, you guarantee efficient operation and longevity, regardless of whether it’s a home or business setting.
What Are the Typical Lifespan Differences for Residential vs. Commercial Systems?
Think of your system as a sturdy tree standing tall through seasons—residential systems often last 10-15 years, while commercial ones can reach 20+ years with proper care. Thanks to technological advancements, commercial heat pumps typically boast greater durability and longer lifespans. Your investment in quality and maintenance directly influences how long your system endures, ensuring consistent comfort and efficiency over the years.
How Do Installation Costs Compare for Residential and Commercial Heat Pumps?
You’ll find that installation costs for residential heat pumps are generally lower due to simpler setup and less complex systems. Commercial systems tend to have a higher cost comparison because they require more extensive installation, specialized equipment, and sometimes structural modifications. The installation complexity for commercial units is greater, which adds to labor and material costs. Overall, expect residential installations to be more budget-friendly, but commercial systems offer greater capacity and durability.
Are There Specific Building Codes Affecting Commercial Heat Pump Installation?
You should know that over 80% of commercial installations are impacted by specific building codes and zoning regulations. These codes often set strict requirements for safety, energy efficiency, and environmental standards, which can influence system size, placement, and safety features. It is crucial to review local building codes before installation, as non-compliance can lead to penalties or delays, ensuring your commercial heat pump meets all legal standards.
Can Residential Heat Pumps Be Scaled for Larger Commercial Applications?
Yes, you can scale residential heat pumps for larger commercial applications, but you’ll face scaling challenges. These systems often aren’t designed for the higher capacity or continuous operation needed in commercial settings. You’ll need to guarantee system compatibility, possibly by modifying components or integrating multiple units. It’s crucial to assess whether the existing design can handle increased loads without compromising efficiency or durability.
Conclusion
Choosing between residential and commercial heat pump systems depends on your specific needs, space, and energy goals. While the right system can efficiently keep your environment comfortable, remember that “the proof of the pudding is in the eating.” Investing wisely means understanding these differences and selecting a system that offers durability and efficiency. Ultimately, making informed decisions today guarantees comfort and savings tomorrow.









