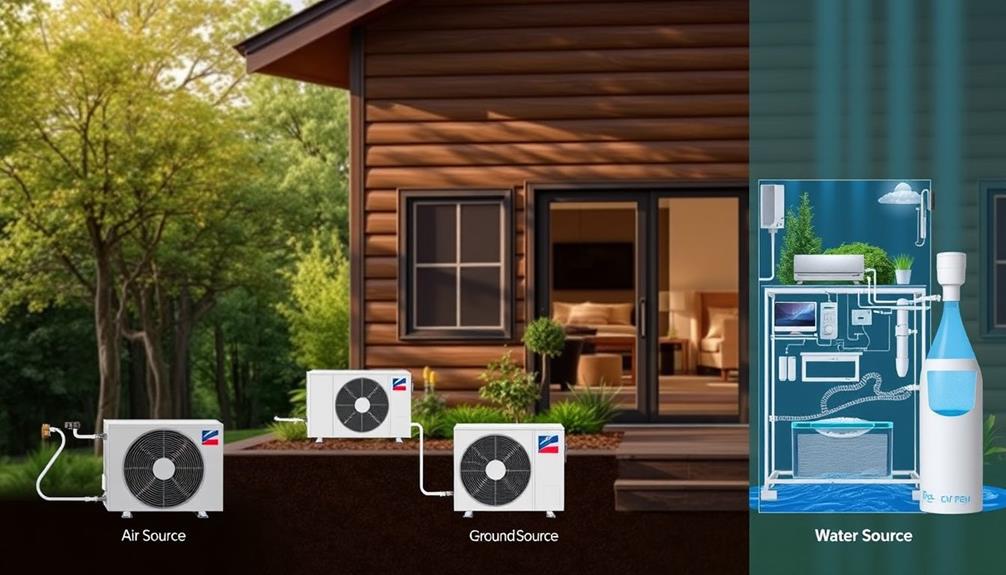
Understanding the different types of heat pumps is essential for your energy efficiency and cost savings. Air-source heat pumps are versatile for mild climates, while ductless mini-split systems offer flexibility without ductwork. If you're in a colder area, consider geothermal pumps for their long-term savings, despite the higher initial costs. Hybrid systems combine traditional heating methods with modern heat pump technology to maximize efficiency. Each option has unique benefits depending on your home's needs. Explore these choices further to discover which heat pump fits your lifestyle best and how it can enhance your comfort year-round.
Key Takeaways
- Consider local climate: Air-source heat pumps are ideal for mild climates, while geothermal and cold climate heat pumps suit colder regions.
- Evaluate existing infrastructure: Ducted systems are best for homes with ductwork; ductless mini-split systems offer flexibility for those without ducts.
- Analyze installation costs versus savings: Geothermal heat pumps have higher upfront costs but provide significant long-term energy savings.
- Look for financial incentives: Federal tax credits and state/local rebates can significantly offset installation costs and improve ROI.
- Consult HVAC professionals: They ensure proper sizing and selection of heat pumps for maximum efficiency and comfort in your home.
What Are Heat Pumps?
When you're looking for an energy-efficient way to heat or cool your home, heat pumps might be the perfect solution. These systems don't generate heat; instead, they transfer it, making them far more efficient than traditional furnaces and boilers.
Heat pumps use energy from the air, water, or ground to move heat indoors or outdoors, achieving effective temperature control, no matter the climate.
One of the standout features of heat pumps is their energy efficiency. They can deliver up to three times more heat energy than the electricity they consume, which means significant savings on your energy bills.
Unlike electric baseboards that rely solely on electrical power, heat pumps make the most of the energy they use, providing a sustainable option for home comfort.
Common causes of heat pump failures can include refrigerant leaks and electrical issues, emphasizing the importance of regular maintenance.
As you consider your options, remember that various types of heat pumps exist, each designed for different environments and installation needs.
Whether you're exploring air-source, water-source, or ground-source solutions, you'll find that heat pumps not only offer excellent performance but also align with modern energy-saving goals.
With federal tax credits and local incentives available, now's a great time to explore this environmentally friendly choice.
Types of Heat Pumps

Heat pumps come in various types, each tailored to meet specific heating and cooling needs. One of the most common options is air-source heat pumps. They extract heat from outdoor air, providing efficient heating and cooling for your home, even in colder climates.
If you're looking for flexibility, mini-split heat pumps allow for individual control in different zones, making them perfect for homes without ductwork. Incorporating natural elements and vintage decor into your workspace can also enhance comfort, much like how tailored heat pump solutions provide personalized climate control.
If you have access to a water source, you might consider water-source heat pumps. These systems are highly efficient, utilizing nearby water bodies for heat transfer, and they work well in multi-unit buildings.
On the other hand, geothermal heat pumps take advantage of the earth's stable underground temperatures. While they boast high efficiency, be prepared for higher upfront installation costs due to the necessary excavation.
For those who want the best of both worlds, hybrid systems combine heat pumps with traditional fossil fuel heating sources. This approach enhances efficiency and offers flexibility, especially during extreme weather.
Air-Source Heat Pumps

Air-source heat pumps are an efficient choice for heating and cooling your home, with the ability to deliver more heat energy than the electricity they consume.
These systems can be especially beneficial in conjunction with other home comfort solutions, such as garage door openers, to enhance overall home security and efficiency.
If you're considering installation, you'll want to weigh the costs and potential savings, especially since you might qualify for federal tax credits.
Plus, even in colder climates, these systems perform well, making them a versatile option for any homeowner.
Efficiency in Heating Cooling
While many homeowners seek efficient solutions for heating and cooling, air-source heat pumps stand out for their impressive energy performance.
These systems can deliver up to three times more heat energy than the electrical energy consumed, making them highly efficient for your home. Additionally, they align with the increasing interest in plant-based diets for health and sustainability by promoting energy-efficient living.
They don't just work well in mild conditions; advanced models maintain performance even at temperatures as low as -5°F.
Here are three key benefits of air-source heat pumps:
- Significant Energy Savings: Ducted air-source heat pumps can reduce electricity use for heating by about 65% compared to traditional electric resistance heating systems.
- Enhanced Comfort: They provide superior dehumidification compared to standard air conditioners, ensuring comfort during humid summer months.
- Financial Incentives: Many air-source heat pumps are eligible for federal tax credits, offering you a financial incentive to invest in energy-efficient heating and cooling solutions.
Installation Considerations and Costs
When considering a switch to an air-source heat pump, installation factors and costs play a significant role in your decision-making process. The average installation cost for these systems is around $5,500, but this can vary based on your home size, insulation quality, and whether you have existing ductwork. If you have ducted heat pumps, you'll likely see a smoother installation process since these systems utilize pre-installed pathways for air distribution.
Here's a quick breakdown of some key factors:
| Factor | Impact on Installation |
|---|---|
| Home Size | Larger homes may incur higher costs |
| Insulation Quality | Better insulation can reduce costs |
| Existing Ductwork | Pre-installed ducts can lower installation time |
Additionally, don't forget to check for local incentives. Many states offer rebates and tax credits that can help offset installation costs, making air-source heat pumps a more financially viable option for homeowners like you. By considering these factors, you can better assess whether an air-source heat pump is the right choice for your needs.
Cold Climate Performance Benefits
Cold Climate Heat Pumps (CCHPs) often excel in harsh winter conditions, making them an ideal choice for homeowners in northern regions.
These advanced systems are designed to maintain high heating capacity even in temperatures as low as -5°F. Additionally, utilizing a balanced approach to home energy efficiency can enhance overall performance, similar to how gout management insights can improve health outcomes.
Here are some key benefits of CCHPs for cold climates:
- Enhanced Efficiency: CCHPs can deliver over twice the heating efficiency of traditional electric resistance systems, providing up to three times more heat energy than the electricity consumed.
- Notable Energy Savings: By integrating a CCHP, you can enjoy energy savings of 50% to 70% compared to conventional heating methods, ultimately reducing your utility bills.
- Variable-Speed Technology: With variable-speed compressors, CCHPs adjust heating output based on outdoor conditions, ensuring peak performance and energy efficiency throughout the winter.
While supplemental heating may be needed during extreme cold spells, advancements in technology have notably improved CCHP performance in subfreezing temperatures.
Ductless Mini-Split Heat Pumps

Ductless mini-split heat pumps offer an efficient solution for heating and cooling your home without the hassle of ductwork.
These systems consist of an outdoor unit paired with one or more indoor units, providing you with flexibility in how you condition your space. Whether it's a chilly Massachusetts winter or a hot summer day, mini-splits deliver effective heating and cooling even in sub-zero temperatures.
Additionally, investing in energy-efficient systems can help you hedge against rising energy costs, similar to how investing in a diversified retirement portfolio can provide long-term financial stability.
One of the standout features of ductless mini-split heat pumps is their energy efficiency. They can achieve up to three times more heating energy than the electricity they consume, which translates to significant savings compared to traditional electric baseboard heating.
Plus, you can enjoy individual temperature control in different zones of your home, ensuring comfort while only conditioning the spaces in use.
If you're considering making the switch, you might be eligible for rebates of up to $10,000 for replacing fossil fuel systems with these advanced heating and cooling systems.
This makes ductless mini-split heat pumps not just an eco-friendly choice but also a financially smart investment for your home.
Geothermal Heat Pumps

If you're exploring efficient heating and cooling options, geothermal heat pumps (GSHP) present an impressive alternative to traditional systems. By utilizing the stable temperatures found underground, these systems can reduce energy use by 70%-80% compared to conventional setups.
Additionally, this technology aligns well with the principles of geothermal energy generation, offering a reliable and eco-friendly energy source. While the upfront installation costs may be higher, the long-term benefits often outweigh this initial investment due to considerably lower operating costs.
When considering geothermal heat pumps, keep these factors in mind:
- Lot Size: You'll need sufficient space for the installation of buried pipes.
- Subsoil Conditions: The type of soil affects heat transfer efficiency, so understanding your landscape is essential.
- Climate Suitability: GSHPs shine in extreme climates, reliably providing consistent heating and cooling.
Given their efficiency and high customer satisfaction, geothermal systems are a solid choice for those looking to invest in sustainable technology.
Just remember, a well-planned installation is key to maximizing your system's performance and benefits. So, evaluate your property and climate conditions carefully to make the most of your geothermal heat pump investment.
Hybrid Heat Pump Systems

Hybrid heat pump systems offer you the best of both worlds by combining air-source heat pumps with traditional gas furnaces.
This setup not only boosts energy efficiency but also adapts to varying climates, ensuring your home stays comfortable year-round.
Additionally, understanding the importance of regular maintenance can enhance the lifespan of your system, similar to how maintenance extends the lifespan of the toilet.
As you consider installation and maintenance, you'll find that these systems can lead to lower overall costs while providing reliable heat during extreme temperatures.
Benefits of Hybrid Systems
Combining the strengths of air-source heat pumps and traditional gas furnaces, hybrid heat pump systems offer an efficient and flexible heating solution tailored to your needs.
These systems adapt to temperature variations, ensuring you enjoy ideal comfort while maximizing energy efficiency. Additionally, it's important to reflect on the financial implications and potential incentives associated with energy-efficient systems, as protecting savings is vital for long-term investment benefits.
Here are three key benefits of hybrid systems:
- Cost Savings: Many users report up to 30% savings on their heating bills compared to traditional methods. The hybrid system uses the most efficient energy source available, reducing your overall energy costs.
- Environmental Impact: By using both electric and gas heating, hybrid systems lower your carbon footprint. This aligns with decarbonization goals, making it a responsible choice for environmentally-conscious homeowners.
- Financial Incentives: Many hybrid heat pump installations qualify for federal tax credits of up to 30%. This makes upgrading to a hybrid system not only an efficient choice but also a financially attractive one.
With these advantages, you can confidently choose a hybrid heat pump system to meet your heating needs while enjoying significant benefits.
Efficiency in Cold Climates
When it comes to heating your home in colder climates, hybrid heat pump systems shine by offering unmatched efficiency.
These systems combine an air-source heat pump with a gas furnace, providing flexibility to adapt to changing temperatures. In extreme cold temperatures, they automatically switch between the heat pump and the gas furnace, ensuring ideal energy use without sacrificing comfort.
Incorporating a holistic lifestyle approach, such as stress management techniques, can further enhance your comfort during the winter months.
Hybrid systems are particularly effective in northern climates, boasting heating capacities that can exceed traditional electric resistance heating by more than double.
During prolonged cold spells, many models can operate down to -5°F or lower without needing auxiliary heat. This means you won't have to worry about your home becoming uncomfortably cold.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Proper installation and maintenance are essential for maximizing the efficiency and longevity of hybrid heat pump systems.
When considering a hybrid system, you need to assess your home's infrastructure, including ductwork and the availability of a gas line for the furnace component.
Here are three key considerations for installation and maintenance:
- Proper Sizing: Confirm the hybrid heat pump is correctly sized for your home. An improperly sized system can lead to inefficiencies and increased energy costs.
- Regular Maintenance Checks: Schedule routine maintenance for both the heat pump and gas furnace. This includes cleaning filters, checking refrigerant levels, and inspecting the gas lines to maintain peak performance.
- Incentives and Costs: Look into local and federal incentives for installing hybrid systems. These can greatly reduce your installation costs, especially if you're shifting from traditional fossil fuel systems.
Energy Efficiency Considerations
Heat pumps stand out as a remarkably efficient option for home heating and cooling, considerably reducing energy consumption. By using heat pump technology, you can cut your electricity use for heating by about 65% compared to traditional methods. This means you'll not only save on your energy bills but also contribute to a more sustainable environment.
Air-source heat pumps are particularly impressive, delivering up to three times more heat energy than the electricity they consume, making them an exceptional choice for residential heating and cooling. If you're looking for even greater savings, geothermal heat pumps can achieve energy savings of 70%-80% by tapping into the stable underground temperatures.
Recent advancements in heat pump technology, like two-speed compressors and variable-speed motors, have further enhanced efficiency and performance. These improvements are especially beneficial in colder climates, ensuring your home remains comfortable without excessive energy use.
Starting in January 2023, the U.S. Department of Energy implemented new efficiency standards that require heat pumps to meet minimum ratings of 14.3 SEER2 and 7.5 HSPF2, ensuring you can find high-performing, energy-efficient options for your home.
Financial Incentives and Rebates

Numerous financial incentives and rebates are available to make the change to heat pumps more affordable for homeowners. By taking advantage of these programs, you can considerably lower your installation costs.
Here are three key financial incentives to take into account:
- Federal Tax Credit: The Inflation Reduction Act offers a 30% federal tax credit on installation costs for heat pumps, with a maximum credit of $2,000 for air-source systems and no cap for geothermal systems until 2032.
- State and Local Rebates: Many states and local utilities provide additional rebates and low-interest loans to further incentivize the adoption of heat pumps, reducing your overall expenses.
- Special Programs: For example, in Oregon, landlords installing heat pumps in rental properties can access specific programs designed to enhance energy efficiency in multifamily housing.
Being aware of these financial incentives and tax credits can considerably influence your decision to shift to heat pump systems.
The potential savings can lead to a quicker return on investment, making this energy-efficient choice even more appealing.
Check local utility programs and resources like the Database of State Incentives for Renewables & Efficiency to find specific options available in your area.
Choosing the Right Heat Pump

With financial incentives making heat pumps more accessible, it's important to choose the right system for your home.
Start by considering your local climate. If you live in a mild area, an air-source heat pump might work well. For colder regions, look into cold climate heat pumps or geothermal systems, which are designed to perform better in harsh conditions.
Next, evaluate your existing infrastructure. If your home has ductwork, a ducted heat pump is a solid choice. However, if you lack ducts or want to target specific rooms, ductless mini-split systems offer great flexibility and efficiency.
Don't forget to assess installation costs versus potential long-term savings. While geothermal heat pumps might've higher upfront costs due to excavation, they can dramatically decrease energy use over time, making them more cost-effective in the long run.
Lastly, consult with HVAC professionals to guarantee proper sizing and selection. An appropriately sized heat pump maximizes efficiency and comfort while minimizing operational costs.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do I Know What Kind of Heat Pump I Need?
To figure out what heat pump you need, assess your climate, home size, and insulation. Consider your budget and whether you have existing ductwork. Research incentives to help with installation costs.
What Is the Best Type of Heat Pump?
You might think there's one best heat pump, but it really depends on your home's needs. Consider factors like climate, efficiency, and budget. Exploring each type will help you make the right choice for your situation.
How Do I Choose a Heating Pump?
To choose a heating pump, assess your climate and home's infrastructure. Consider energy efficiency ratings and available financial incentives. Consulting HVAC professionals can help you select and install the best system for your needs.
What Brand of Heat Pump Is the Most Reliable?
If your neighbor swears by their Trane heat pump's reliability, you might want to contemplate it too. Trane consistently ranks high in customer satisfaction, making it a top choice for dependable performance in heating systems.
Conclusion
In choosing the right heat pump for your home, consider your needs, assess your options, and evaluate your budget. Whether you opt for an air-source, a ductless mini-split, or a geothermal system, each type brings its own benefits. Embrace energy efficiency, explore financial incentives, and enjoy the comfort you deserve. By making an informed choice, you'll not only enhance your home's climate control but also contribute to a more sustainable future.









