We’ve all felt the necessity for effective heating and cooling solutions, yet were you aware that HVAC systems and heat pumps provide distinct alternatives?
In this article, we explore the key differences between these two options. From understanding the components and working principles to comparing energy efficiency and costs, we delve into the technical details to help you make an informed choice.
So, let’s dive in and uncover the fascinating world of HVAC systems versus heat pumps.
Key Takeaways
- HVAC systems consist of components such as thermostats, furnaces, air conditioners, and air ducts.
- Heat pumps offer energy efficiency, cost savings, and environmental friendliness.
- Heat pumps reduce the need for separate heating and cooling systems.
- Heat pumps are more energy-efficient compared to traditional HVAC systems.
Types of HVAC Systems
In this section, we’ll discuss the different types of HVAC systems.
When it comes to heat pumps, there are three main types: air-source, ground-source, and water-source heat pumps.
Air-source heat pumps are the most common and work by extracting heat from the outside air and transferring it indoors. They can provide both heating and cooling, making them versatile.
Ground-source heat pumps, also known as geothermal heat pumps, utilize the stable temperature of the ground to provide heating and cooling. They’re highly efficient and can reduce energy consumption.
Water-source heat pumps use water as a heat source or heat sink. They’re commonly used in areas with access to a water source, such as lakes or ponds.

The advantages of heat pumps include energy efficiency, cost savings, and environmental friendliness. They can provide both heating and cooling, reducing the need for separate systems. Additionally, they’re more environmentally friendly compared to traditional HVAC systems, as they use renewable energy sources.
Components of HVAC Systems
Now let’s take a closer look at the components of HVAC systems. Understanding the basics of an HVAC system is crucial in order to grasp the functionality of each component.
Key components such as the thermostat, furnace, air conditioner, and air ducts all play a vital role in regulating temperature, maintaining indoor air quality, and ensuring proper airflow throughout the space.
HVAC System Basics
We’ll start by discussing the components of HVAC systems. These systems consist of several key elements that work together to provide heating, ventilation, and air conditioning for a building. Here are the main components you’ll find in an HVAC system:

-
Heating Unit: This is typically a furnace or a heat pump that generates heat to warm the air in the building during colder months. Proper installation and regular maintenance of the heating unit are essential to ensure its efficient and safe operation.
-
Cooling Unit: The cooling unit, usually an air conditioner or heat pump, cools and dehumidifies the air during warmer months. Regular maintenance, such as cleaning the air filters and checking refrigerant levels, can help optimize its performance.
-
Ductwork: Ducts distribute the conditioned air throughout the building. Proper design and insulation of the ductwork are crucial for efficient airflow and temperature control.
Key Components Explained
Let’s dive into the key components of HVAC systems, which include the heating unit, cooling unit, and ductwork.

The heating unit is responsible for generating and distributing heat throughout a space, typically using a furnace or a heat pump.
The cooling unit, on the other hand, removes heat from the air and cools it down using a refrigeration cycle. This unit usually consists of an air conditioner or a heat pump.
Lastly, the ductwork serves as a network of channels that transport heated or cooled air from the HVAC system to different areas of a building.
Analyzing these key components allows us to understand the advantages of heat pumps, such as their ability to provide both heating and cooling functions.

Now, let’s explore the function of each component.
Function of Each Component
Each component of HVAC systems has a specific function that contributes to the overall heating, cooling, and ventilation of a space. Understanding the function of each component is crucial for maintaining the efficiency and effectiveness of the system. Here are the key components and their functions:
-
Thermostat: This component serves as the control center of the HVAC system. It senses the temperature in the space and signals the heating or cooling mechanism to turn on or off accordingly. The thermostat also allows users to set their desired temperature and control the system.
-
Furnace: The furnace is responsible for generating heat in heating mechanisms. It burns fuel, such as natural gas or oil, and uses a heat exchanger to warm the air before distributing it throughout the space.

-
Air Conditioner: The air conditioner cools the air by removing heat and humidity from the space. It uses a refrigeration cycle to transfer heat from inside to outside, creating a comfortable indoor temperature.
Working Principles of HVAC Systems
How do HVAC systems work? HVAC systems, or Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning systems, are designed to provide thermal comfort and maintain indoor air quality in buildings. They function by using energy to control the temperature, humidity, and air distribution within a space.
The working principles of HVAC systems involve a combination of mechanical, electrical, and thermodynamic processes. Here is a breakdown of the main components and their functions:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Furnace | Produces heat by burning fuel or using electricity |
| Heat Exchanger | Transfers heat from the furnace to the air |
| Air Conditioner | Removes heat and humidity from the air |
| Ductwork | Distributes conditioned air throughout the building |
Energy Efficiency of HVAC Systems
To assess the energy efficiency of HVAC systems, we need to compare their performance to industry standards and consider factors such as equipment efficiency, insulation, and maintenance.

Here are three key considerations when evaluating the energy efficiency of HVAC systems:
-
Equipment Efficiency: The efficiency of the HVAC equipment, such as the air conditioner and furnace, directly impacts energy savings. Higher-rated equipment consumes less energy, resulting in lower utility bills and reduced environmental impact.
-
Insulation: Proper insulation plays a crucial role in preventing heat loss or gain, ensuring that the HVAC system doesn’t have to work harder to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature. Well-insulated buildings require less energy for heating and cooling, leading to significant energy savings.
-
Maintenance: Regular maintenance of the HVAC system is essential for optimal energy efficiency. Dirty filters, leaky ducts, and faulty components can result in decreased performance and increased energy consumption. Routine maintenance helps identify and address issues promptly, maximizing energy savings and minimizing the system’s environmental impact.
Considering these factors, HVAC systems can achieve significant energy savings and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Now let’s explore the benefits of heat pumps.
Benefits of Heat Pumps
We can highlight the benefits of heat pumps by examining their energy efficiency, versatility, and cost savings.
Heat pumps are known for their exceptional energy efficiency, making them an environmentally friendly choice for heating and cooling. They operate by transferring heat from one place to another, rather than generating heat through combustion, resulting in lower energy consumption. This not only reduces carbon emissions but also helps homeowners save on their energy bills.

In addition to their energy efficiency, heat pumps are versatile and can be used for both heating and cooling purposes. They can extract heat from the air, ground, or water, providing efficient heating and cooling solutions in various climates.
With their energy-saving capabilities and versatility, heat pumps offer significant benefits to homeowners and contribute to a more sustainable future.
As we explore the differences in heating capabilities, it’s important to understand the advantages that heat pumps bring to the table.
Differences in Heating Capabilities
When comparing the heating capabilities of HVAC systems and heat pumps, there are several important points to consider.

First, efficiency is a crucial factor to examine as it directly affects energy consumption and costs.
Second, cost considerations play a significant role in determining which option is more suitable for your specific needs and budget.
Lastly, climate suitability should be taken into account, as different regions have varying heating demands and conditions that may favor one system over the other.
Efficiency Comparison: HVAC Vs. Heat Pumps
How do HVAC systems and heat pumps differ in terms of their heating capabilities? Here are three key points to consider when comparing their efficiency:

-
Environmental Impact: Heat pumps are more environmentally friendly compared to traditional HVAC systems. Heat pumps use electricity to transfer heat rather than burning fossil fuels, resulting in lower carbon emissions and a reduced impact on the environment.
-
Heating Efficiency: Heat pumps are highly efficient in moderate climates, as they can extract heat from the outside air even in colder temperatures. However, in extremely cold climates, the heating efficiency of heat pumps decreases, and HVAC systems may provide better heating capabilities.
-
Maintenance Comparison: HVAC systems require regular maintenance, including filter replacement and system inspections, to ensure proper functioning. On the other hand, heat pumps require similar maintenance but also need regular defrosting to remove ice buildup during colder weather.
Considering these efficiency factors, it’s important to weigh the environmental impact, heating efficiency, and maintenance requirements when deciding between HVAC systems and heat pumps.
Now, let’s delve into the cost considerations of HVAC systems versus heat pumps.
Cost Considerations: HVAC Vs. Heat Pumps
To compare the cost considerations between HVAC systems and heat pumps in terms of their heating capabilities, let’s examine the differences.
One important factor to consider is energy consumption. Heat pumps are known to be more energy-efficient compared to traditional HVAC systems. Heat pumps use electricity to transfer heat from one place to another, rather than generating heat directly. This allows them to consume less energy while still providing adequate heating. On the other hand, HVAC systems require fuel, such as natural gas or oil, to generate heat. This can result in higher energy consumption and increased costs over time.
Additionally, installation costs can vary between the two systems. Heat pumps typically have higher upfront installation costs due to the need for specialized equipment and labor. HVAC systems, on the other hand, may have lower upfront costs but can have higher long-term maintenance and repair expenses.
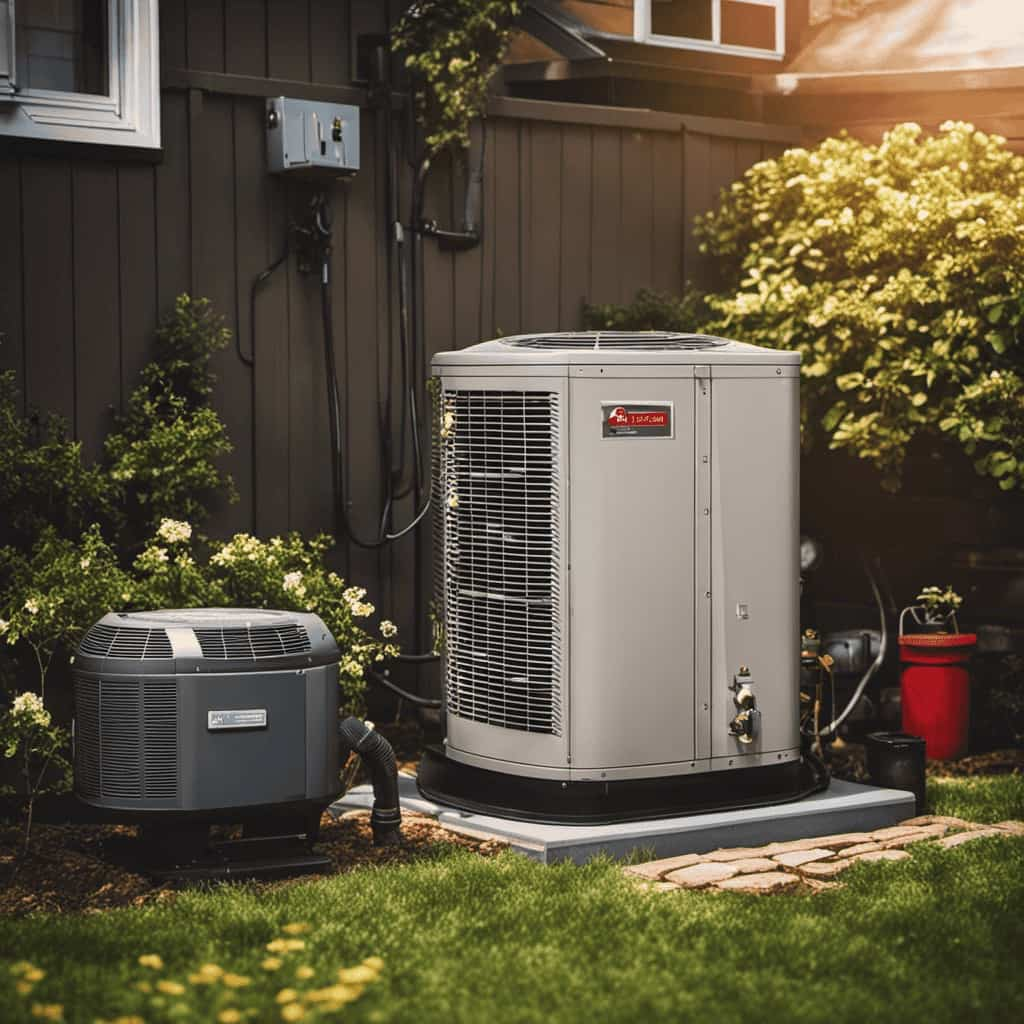

Climate Suitability: HVAC Vs. Heat Pumps
One key difference in heating capabilities between HVAC systems and heat pumps is their suitability for different climates. The geographical limitations of HVAC systems make them more suitable for regions with extreme temperature fluctuations, such as areas with hot summers and cold winters.
On the other hand, heat pumps are ideal for climates with mild winters, as they rely on extracting heat from the outside air and transferring it indoors. This makes heat pumps more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly compared to HVAC systems, which use fuel combustion to generate heat.
However, in extremely cold climates, heat pumps may struggle to extract enough heat from the outdoor air, reducing their efficiency.
Transitioning into the subsequent section about the cooling performance of HVAC systems, it’s important to consider how these systems can effectively cool indoor spaces.

Cooling Performance of HVAC Systems
We rely on HVAC systems for the cooling performance in our homes during the hot summer months. HVAC systems are designed to provide efficient cooling and precise temperature control.
Cooling efficiency is a key factor in the performance of these systems, as it determines how effectively they can cool the indoor space while consuming minimal energy. HVAC systems achieve high cooling efficiency through the use of advanced technology such as variable speed compressors and smart thermostats.
These systems can quickly lower the indoor temperature to the desired level and maintain it consistently, ensuring optimal comfort.
As we move on to the next section, we’ll now explore the cost comparison between HVAC systems and heat pumps, considering factors such as installation, maintenance, and energy consumption.

Cost Comparison: HVAC Systems Vs Heat Pumps
When comparing the costs of HVAC systems and heat pumps, it’s important to consider factors such as installation, maintenance, and energy consumption. Here is a breakdown of the cost comparison between the two systems:
-
Installation expenses: HVAC systems typically require more extensive installation procedures, including ductwork and air distribution systems. This can result in higher upfront costs compared to heat pumps, which often have simpler installation requirements.
-
Maintenance: HVAC systems may require more frequent maintenance due to the complexity of their components, such as filters, motors, and compressors. Heat pumps, on the other hand, have fewer moving parts and may require less maintenance over time.
-
Long-term savings: Heat pumps are known for their energy efficiency, as they transfer heat from the outside air to warm the interior space. This can lead to significant long-term savings on energy bills compared to HVAC systems.

Considering these factors, heat pumps may offer lower installation expenses and long-term savings compared to HVAC systems. However, it’s essential to evaluate your specific needs and consult with a professional to determine the most cost-effective solution for your home.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can HVAC Systems Be Used for Both Heating and Cooling Purposes?
Yes, HVAC systems can be used for both heating and cooling purposes. However, heat pumps have distinct advantages for heating and cooling, such as higher energy efficiency compared to HVAC systems.
How Long Do HVAC Systems Typically Last Before Needing to Be Replaced?
HVAC systems typically last for about 15 to 20 years before needing replacement. However, signs of system failure like frequent breakdowns, inadequate cooling or heating, and increased energy bills may indicate the need for earlier replacement.
Are There Any Government Incentives or Rebates Available for Installing HVAC Systems or Heat Pumps?
Government incentives and rebates are available for installing HVAC systems and heat pumps. These programs aim to promote energy efficiency, reduce costs, and minimize environmental impact. The installation process and cost analysis should consider these incentives.

Can HVAC Systems and Heat Pumps Be Integrated With Smart Home Technology?
Yes, HVAC systems and heat pumps can be integrated with smart home technology. However, there are some integration challenges to consider. The benefits of smart home technology include increased energy efficiency and convenience.
What Maintenance and Upkeep Is Required for HVAC Systems and Heat Pumps to Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity?
Maintenance tips and regular servicing are crucial for optimal performance and longevity of HVAC systems and heat pumps. Neglecting maintenance can lead to decreased efficiency, higher energy costs, and potential system failures.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while HVAC systems and heat pumps both provide heating and cooling functions, they differ in their heating capabilities and energy efficiency.
HVAC systems use a combination of heating and cooling units, whereas heat pumps are designed solely for heating purposes. Additionally, heat pumps offer greater energy efficiency by utilizing renewable energy sources.

Therefore, when considering the cost and environmental impact, heat pumps are a more sustainable choice.









