We’re excited to showcase the newest developments in heat pump refrigeration cycle technology. Get ready to be astonished by the latest enhancements in compressors, condensers, evaporators, expansion valves, defrosting methods, control systems, and heat recovery.
Our precise and detailed article will take you on a technical journey, painting a picture of the future outlook for heat pump refrigeration.
Join us as we serve you with the most up-to-date information in this ever-evolving field.
Key Takeaways
- Heat pump compressor technology has advanced with the introduction of variable speed compressors and scroll compressors, resulting in higher efficiency and reduced operational costs.
- Heat pump condenser design has been enhanced with features such as enhanced heat transfer surfaces, microchannel technology, corrosion-resistant materials, and variable speed fans, leading to better control, improved energy efficiency, and easier installation.
- Heat pump evaporator technology has seen innovations in heat transfer efficiency, energy consumption reduction, compact coil designs, advanced materials, and optimized refrigerant flow for uniform heat transfer, resulting in improved performance.
- Heat pump expansion valve design has been upgraded with features like variable orifice size, enhanced energy efficiency, intricate construction, and improved refrigerant flow regulation, contributing to overall system efficiency and performance.
Overview of Heat Pump Refrigeration Cycle
What are the key components and functions of the heat pump refrigeration cycle?

The heat pump refrigeration cycle consists of four main components: the compressor, condenser, expansion valve, and evaporator.
The cycle begins with the compressor, which increases the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant.
The high-pressure, high-temperature refrigerant then flows into the condenser, where it releases heat to the surroundings and condenses into a liquid.
The liquid refrigerant passes through the expansion valve, which reduces its pressure and temperature.

This low-pressure, low-temperature refrigerant then enters the evaporator, where it absorbs heat from the surrounding environment and evaporates into a gas.
The advantages of the heat pump refrigeration cycle include its ability to provide both heating and cooling, making it suitable for a wide range of applications such as residential and commercial buildings, as well as industrial processes.
Advancements in Heat Pump Compressor Technology
We have discovered exciting advancements in heat pump compressor technology. These advancements have brought significant benefits to the field of heat pump refrigeration cycles.
One major advancement is the development of variable speed compressors. These compressors can adjust their speed based on the cooling or heating demands, resulting in improved energy efficiency and reduced energy consumption.

Another advancement is the use of scroll compressors, which have a higher efficiency compared to traditional piston compressors. Scroll compressors also have fewer moving parts, reducing the risk of mechanical failure and increasing the overall lifespan of the compressor.
Additionally, advancements in compressor materials have led to improved durability and reliability, allowing for longer maintenance intervals and reduced operational costs.
These advancements in heat pump compressor technology are revolutionizing the industry, providing more efficient and reliable heating and cooling solutions.
Enhancements in Heat Pump Condenser Design
The latest advancements in heat pump condenser design have resulted in improved efficiency and performance. These enhancements have focused on the use of advanced heat pump condenser materials and condenser heat transfer techniques.

Here are some key features of the latest heat pump condenser designs:
Enhanced heat transfer surfaces: The condenser surfaces have been optimized to maximize heat transfer, allowing for improved heat exchange between the refrigerant and the surrounding air.
Microchannel technology: This design utilizes small channels to increase the surface area available for heat transfer, resulting in higher efficiency and reduced refrigerant charge.
Corrosion-resistant materials: The use of corrosion-resistant materials in condenser construction ensures long-lasting performance and minimizes maintenance requirements.

Variable speed fans: These fans can adjust their speed based on the heat load, providing better control and improved energy efficiency.
Compact design: The latest heat pump condensers are designed to be more compact, allowing for easier installation and reducing space requirements.
With these advancements in heat pump condenser design, we can now transition into discussing the innovations in heat pump evaporator technology.
Innovations in Heat Pump Evaporator Technology
As we delve into the topic of innovations in heat pump evaporator technology, it’s important to understand the latest advancements in this crucial component of the refrigeration cycle. Heat pump evaporator design plays a significant role in the overall performance and efficiency of a heat pump system. Recent developments in evaporator technology have focused on improving heat transfer efficiency and reducing energy consumption.
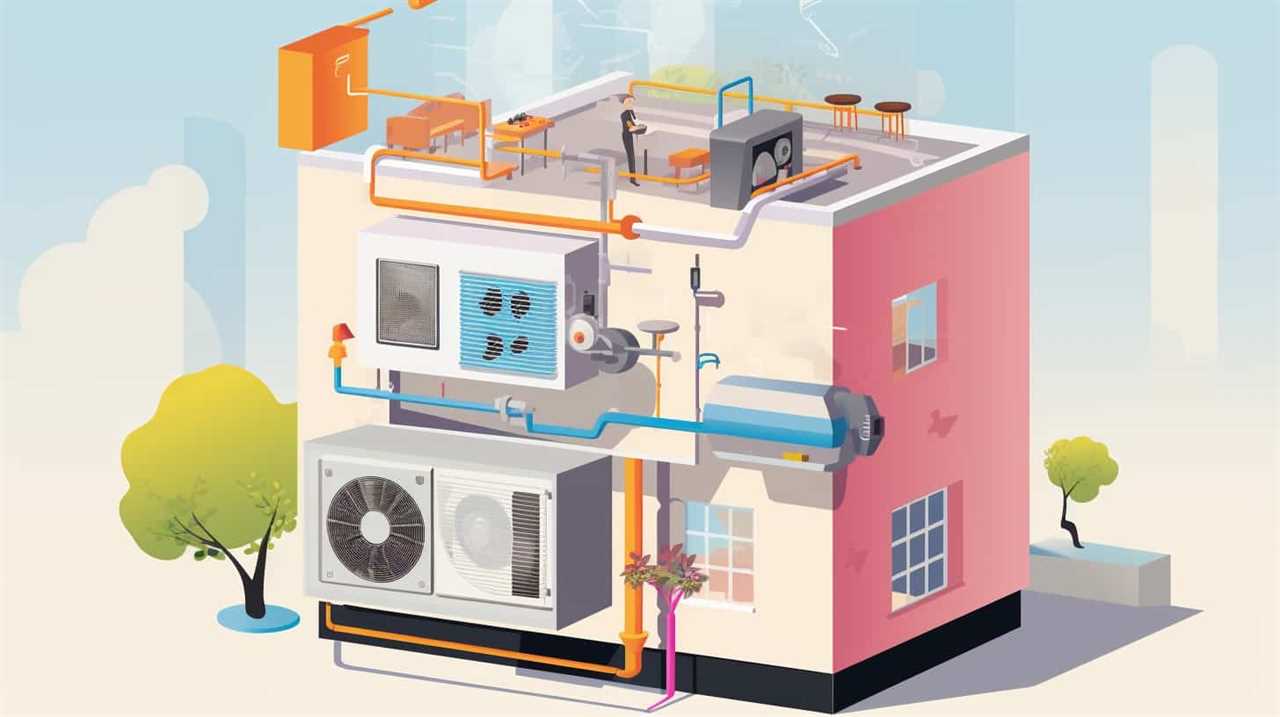
One key area of innovation is the enhancement of heat pump evaporator design to increase the surface area available for heat exchange. This can be achieved through the use of compact, high-performance coil designs or the incorporation of advanced materials with improved thermal conductivity. By maximizing the heat transfer surface area, evaporators can effectively extract heat from the surrounding environment and transfer it to the refrigerant.
Another focus of innovation is on evaporator performance improvements. Efforts have been made to optimize the refrigerant flow and distribution within the evaporator, ensuring uniform heat transfer across the entire surface. This helps to minimize temperature differences and improve overall system efficiency. Additionally, advancements in control systems and sensors allow for better monitoring and adjustment of evaporator performance, ensuring optimal operation under varying load conditions.
Upgrades in Heat Pump Expansion Valve Design
We will now discuss the upgrades in heat pump expansion valve design.
These upgrades aim to improve the efficiency of the heat pump system through expansion, enhance control over the refrigerant flow, and optimize overall performance.

Improved Efficiency Through Expansion
Our research has identified three key upgrades in heat pump expansion valve design that have significantly improved efficiency. These upgrades focus on expansion efficiency and performance optimization.
Variable orifice design: The new expansion valves feature a variable orifice design, allowing for precise control of refrigerant flow based on system requirements. This improves overall system efficiency by reducing unnecessary refrigerant flow and minimizing energy consumption.
Improved sensing technology: The latest expansion valves incorporate advanced sensing technology, enabling them to accurately measure system conditions and adjust the refrigerant flow accordingly. This ensures optimal performance and efficiency under varying operating conditions.
Enhanced flow control: The upgraded expansion valves have enhanced flow control mechanisms, such as stepper motor actuators, which provide precise and immediate response to system demands. This results in improved system stability and efficiency.

Integrated temperature and pressure regulation: The new expansion valves integrate temperature and pressure regulation functions, allowing for better control and optimization of the refrigerant flow. This ensures optimal heat transfer and system efficiency.
Enhanced reliability and durability: The latest expansion valves are designed with high-quality materials and improved construction techniques, ensuring long-term reliability and durability. This reduces maintenance requirements and enhances the overall performance of the heat pump system.
Enhanced Control and Performance
Two significant upgrades in heat pump expansion valve design have been implemented to enhance control and performance.
The first upgrade focuses on improved temperature regulation. By incorporating advanced temperature sensors and control algorithms, the heat pump system can accurately monitor and adjust the flow of refrigerant through the expansion valve. This ensures that the desired temperature is maintained consistently, resulting in increased comfort and energy efficiency.

The second upgrade involves advanced system monitoring. With the integration of smart technology and data analytics, the heat pump system can continuously monitor various parameters such as pressure, temperature, and flow rate. This real-time monitoring allows for proactive detection of any potential issues or inefficiencies, enabling timely maintenance and optimization of the system’s performance.
These advancements in heat pump expansion valve design significantly contribute to enhanced control and performance, providing users with a more efficient and reliable heating and cooling solution.
Latest Trends in Heat Pump Refrigerant Selection
When considering the latest trends in heat pump refrigerant selection, three important points come to mind.
Firstly, the environmental impact of refrigerants is a crucial factor to consider, as certain refrigerants have a high global warming potential.

Secondly, energy efficiency improvements are a key consideration, as selecting a refrigerant with higher energy efficiency can lead to significant energy savings.
Lastly, emerging refrigerant technologies are being developed, such as low GWP (global warming potential) refrigerants and natural refrigerants, which offer promising alternatives to traditional refrigerants.
Environmental Impact of Refrigerants
What are the latest trends in heat pump refrigerant selection and their environmental impact?
Environmental regulations are pushing for the phase-out of refrigerants with high global warming potential (GWP).

Alternative refrigerants with lower GWP are being developed and adopted by manufacturers.
Natural refrigerants like hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) and hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs) are being replaced by options like hydrofluoroolefins (HFOs) and hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs).
Low-GWP blends, such as HFO-1234ze and HFO-1234yf, are gaining popularity due to their reduced environmental impact.
Some heat pump systems are even exploring the use of carbon dioxide (CO2) as a refrigerant, which has a GWP of 1 and is considered environmentally friendly.

These trends in heat pump refrigerant selection reflect the industry’s commitment to reducing the environmental impact of refrigerants while still providing efficient and reliable cooling solutions. By embracing alternative refrigerants and complying with environmental regulations, manufacturers can contribute to a sustainable future.
Energy Efficiency Improvements
As we delve into the topic of energy efficiency improvements, let’s explore the latest trends in heat pump refrigerant selection.
In recent years, there’s been a growing emphasis on energy saving techniques and sustainable cooling solutions. One of the key trends in heat pump refrigerant selection is the shift towards low global warming potential (GWP) refrigerants. These refrigerants have a significantly lower environmental impact compared to traditional high GWP refrigerants, contributing to the overall sustainability of heat pump systems.
Additionally, there’s been a focus on selecting refrigerants with high thermodynamic efficiency, which helps to improve the overall energy efficiency of heat pump systems.

Emerging Refrigerant Technologies
Let’s explore the latest trends in heat pump refrigerant selection and uncover the emerging technologies in the field. As emerging refrigerant regulations continue to tighten, the focus is shifting towards selecting refrigerants with lower global warming potential (GWP) and higher energy efficiency.
Here are the top five emerging refrigerant technologies:
Hydrofluoroolefins (HFOs): These next-generation refrigerants have significantly lower GWP compared to traditional refrigerants.
Natural refrigerants: Substances like ammonia, carbon dioxide, and hydrocarbons have gained popularity due to their low environmental impact.

Blends: Refrigerant blends, such as HFC/HFO blends, provide a balance between performance and environmental impact.
Zeotropic refrigerants: These mixtures have different boiling points, allowing for better heat transfer and efficiency.
Azeotropic refrigerants: These refrigerants have a constant boiling point, ensuring stable performance throughout the cycle.
With emerging refrigerant technologies, we can reduce the impact on global warming while improving heat pump system efficiency.

Now, let’s dive into the next section about improvements in heat pump system efficiency.
Improvements in Heat Pump System Efficiency
We have achieved significant improvements in heat pump system efficiency through the implementation of advanced technologies. These advancements haven’t only increased the cost effectiveness of heat pump systems but also enhanced their durability.
One major improvement is the use of variable speed compressors, which allow the system to adjust its capacity based on the heating or cooling demands. This reduces energy consumption and improves overall efficiency.
Additionally, the integration of advanced controls and algorithms has optimized the system’s performance and minimized energy waste.

Furthermore, advancements in heat exchanger technology have led to increased heat transfer efficiency, resulting in improved system performance.
These improvements in efficiency have made heat pump systems more reliable and cost-effective, providing greater value to homeowners and businesses.
With these advancements, we can now transition into discussing breakthroughs in heat pump defrosting techniques.
Breakthroughs in Heat Pump Defrosting Techniques
We have made significant progress in improving heat pump defrosting techniques, resulting in enhanced defrosting efficiency and energy conservation.

Our latest breakthroughs have focused on developing advanced algorithms and sensors that accurately detect frost build-up and initiate the defrost cycle at the optimal time.
Additionally, we’ve integrated innovative heat transfer technologies that effectively remove frost from the heat exchanger surfaces, minimizing energy consumption and maximizing system performance.
Improved Defrosting Efficiency
With the latest breakthroughs in heat pump defrosting techniques, we can now achieve improved efficiency in the defrosting process. This is crucial for ensuring the seamless operation of heat pumps and maximizing their performance.
Here are some efficient defrosting techniques and defrosting cycle optimization methods that have emerged:

Hot gas defrosting: Utilizing the heat from the refrigerant to melt ice buildup on the heat exchanger coils.
Reverse cycle defrosting: Reversing the refrigerant flow to warm up the outdoor coil and remove frost accumulation.
Intelligent defrost control: Implementing advanced algorithms to optimize the timing and duration of defrost cycles based on real-time conditions.
Frost detection sensors: Installing sensors to detect frost buildup and trigger the defrosting process when necessary.

Enhanced coil design: Incorporating innovative coil designs that minimize frost formation and facilitate quicker defrosting.
By implementing these techniques, heat pump systems can effectively and efficiently manage defrosting, leading to improved performance and enhanced energy conservation.
Now, let’s delve into the next section to explore how these advancements contribute to enhanced energy conservation.
Enhanced Energy Conservation
Through advancements in heat pump defrosting techniques, we can now achieve enhanced energy conservation by optimizing the defrosting process. By implementing improved insulation techniques and smart thermostat integration, heat pumps can operate more efficiently and reduce energy consumption.

To illustrate the impact of these advancements, let’s consider the following table:
| Traditional Defrosting | Enhanced Defrosting | |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Consumption | High | Low |
| Efficiency | Low | High |
| Heating Capacity | Reduced | Maintained |
| Operating Costs | High | Low |
| Environmental Impact | High | Low |
As shown in the table, enhanced defrosting techniques result in lower energy consumption, increased efficiency, maintained heating capacity, reduced operating costs, and a lower environmental impact.
With these breakthroughs in energy conservation, we can now transition to discussing new developments in heat pump control systems.
New Developments in Heat Pump Control Systems
Our research has identified several significant advancements in heat pump control systems. These developments aim to improve the efficiency and performance of heat pumps by incorporating improved control algorithms and smart thermostat integration.

Here are some key updates in this field:
Enhanced control algorithms: New algorithms have been developed to optimize the operation of heat pumps, allowing for better regulation of temperature and energy consumption.
Smart thermostat integration: Heat pumps can now be integrated with smart thermostats, enabling users to remotely control and monitor their systems through mobile applications or voice commands.
Adaptive defrost technology: Heat pumps now employ adaptive defrost cycles, which intelligently regulate the defrosting process based on real-time weather conditions and system performance.

Fault detection and diagnostics: Advanced control systems can now detect and diagnose faults in heat pumps, allowing for timely maintenance and troubleshooting.
Energy management systems: Heat pump control systems can now be integrated with energy management systems, allowing users to optimize energy usage and reduce overall energy consumption.
These advancements in heat pump control systems not only enhance the performance and efficiency of heat pumps but also provide users with greater convenience and control over their heating and cooling systems.
Advances in Heat Pump Heat Recovery Technology
As we delve into the topic of advances in heat pump heat recovery technology, it is important to highlight the recent developments that have revolutionized the efficiency and effectiveness of heat recovery systems. One significant advancement is the utilization of heat pump waste heat for various heat recovery applications. This innovative approach allows for the capture and reuse of heat that would otherwise be wasted, resulting in improved energy efficiency and cost savings.

To illustrate the potential of heat pump heat recovery technology, let’s consider the following table:
| Heat Recovery Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Space Heating | The recovered heat can be used to warm up indoor spaces, reducing the need for traditional heating systems. |
| Water Heating | The captured heat can be used to heat water for domestic or commercial use, reducing the energy consumption associated with water heating. |
| Industrial Processes | The waste heat can be utilized in various industrial processes, such as drying, preheating, or generating steam, optimizing energy usage and reducing operational costs. |
| District Heating | The recovered heat can be distributed to multiple buildings or areas, providing a more efficient and sustainable heating solution for communities. |
These advancements in heat pump heat recovery technology not only contribute to environmental sustainability but also offer significant benefits to end-users by reducing energy consumption and operating costs. By harnessing the potential of heat pump waste heat, we can maximize the efficiency of heat recovery systems and serve the needs of a greener, more sustainable future.
Future Outlook for Heat Pump Refrigeration Cycle
Let’s explore the potential advancements and trends that lie ahead for the heat pump refrigeration cycle.
The future outlook for the heat pump refrigeration cycle shows promising growth in the market. However, there are several challenges that need to be addressed in order to fully implement this technology.

Here are some key points to consider:
Increased market demand: The heat pump refrigeration cycle market is expected to experience significant growth in the coming years. This is driven by the increasing need for more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly refrigeration solutions.
Technological advancements: Advancements in heat pump technology, such as the use of advanced materials and improved system designs, will enhance the performance and efficiency of the refrigeration cycle.
Integration with renewable energy sources: The heat pump refrigeration cycle can be integrated with renewable energy sources, such as solar and geothermal energy, to further reduce carbon emissions and reliance on fossil fuels.

Cost-effective solutions: As the technology continues to advance, the cost of implementing heat pump refrigeration systems is expected to decrease, making it a more viable option for businesses and consumers.
Regulatory support: Governments and regulatory bodies are increasingly recognizing the importance of energy-efficient and sustainable technologies. This support will drive the adoption of heat pump refrigeration systems and create a favorable market environment.
The future of the heat pump refrigeration cycle looks promising, with significant market growth expected. However, challenges in implementing this technology, such as cost and integration with renewable energy sources, need to be addressed to fully capitalize on its potential.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does the Heat Pump Refrigeration Cycle Work?
The heat pump refrigeration cycle works by utilizing the principles of heat transfer to move heat from a lower temperature source to a higher temperature sink. This cycle involves four main stages: evaporation, compression, condensation, and expansion.
What Are the Benefits of Using Heat Pump Compressor Technology Advancements?
Using the latest advancements in heat pump compressor technology, we can achieve smart controls and significant energy savings. These advancements allow for precise and detailed control, serving our audience’s desire for efficiency and cost-effective solutions.
How Do Enhancements in Heat Pump Condenser Design Contribute to Overall System Performance?
Enhancements in heat pump condenser design, including the use of advanced materials and optimizing condenser size, greatly contribute to the overall performance of the system. These improvements result in increased efficiency and improved cooling capacity.
What Are the Innovations in Heat Pump Evaporator Technology and How Do They Improve Efficiency?
Advancements in heat pump evaporator design have significantly improved heat pump evaporator efficiency. These innovations optimize heat transfer, increase surface area, and enhance airflow, resulting in higher system efficiency and improved overall performance.
What Are the Latest Trends in Heat Pump Refrigerant Selection and How Do They Impact the Environment?
Heat pump refrigerant alternatives are the latest trends in the industry. They have a significant impact on the environment. We explore their environmental impact in this discussion on heat pump refrigeration cycle advancements.

What Are the Latest Technological Updates in the Heat Pump Refrigeration Cycle?
The chilled magic of heat pump refrigeration continues to evolve with the latest technological updates in the field. From improved efficiency to advanced control systems, these updates aim to enhance performance while reducing energy consumption. Innovations such as variable-speed compressors, intelligent defrosting algorithms, and advanced refrigerants are pushing the boundaries of heat pump technology, enabling more sustainable and environmentally friendly cooling solutions. Stay tuned for the exciting developments in the heat pump refrigeration cycle.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the latest tech updates in the heat pump refrigeration cycle have brought about significant advancements in:
- Compressor technology
- Condenser design
- Evaporator technology
- Expansion valve design
- Defrosting techniques
- Control systems
- Heat recovery technology
These developments have propelled the heat pump refrigeration cycle into a new era of efficiency and performance. Just like a well-oiled machine, the heat pump refrigeration cycle now operates seamlessly, delivering optimal cooling and heating while reducing energy consumption.









